Between 2019 and 2020, reportage of Phishing and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) grew by 40%, while identity theft, merchant fraud, malware, and cyber espionage grew by 20%, as per CERT-In study. With such increasing trends, Cybersecurity in fintech has become one of the most critical pain points of the industry, especially in a growing economy like India which is at the cusp of digitalization. With an increasing number of financial services hopping on to the technology bandwagon and more patrons choosing digital modes of payments, the risks of online fraud, information theft, virus attacks, and identity cloning are only going to further increase in the coming days.
Attackers’ playbook includes applications and web portals with compromised cybersecurity; and cyberattacks appear in the form of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), ransomware, application vulnerability exploits, merchant frauds, spam, and reconnaissance attacks. Other examples of cybersecurity threats include software supply chain attacks and account takeovers (Fig. 1)
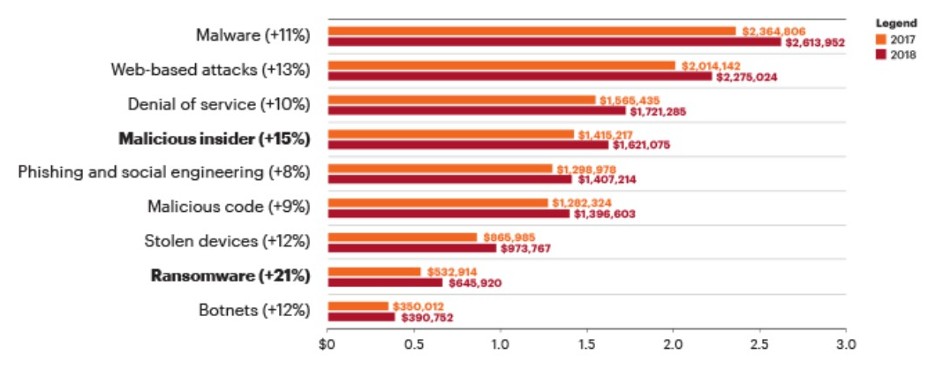
Not only can such attacks cause serious financial loss, but also lead to a dent in the brand’s value apart from paralyzing infrastructure and critical customer-oriented services. Therefore, along with the diverse and deep digital experience, there is also a critical need to secure a business and its customers from damaging, costly, and frequent cybersecurity incidents. Software Supply Chain Security (SSCS) or third-party security risk management is at the core of every fintech’s agenda. Cybersecurity is now given high priority status at product design and decision-making levels across Information Security Professionals and fintech companies’ leadership teams. But what are the fintech security challenges that companies face?
Some of the current fintech risks and challenges concerning cybersecurity
- Identity Management- When a user subscribes or registers to an app, a fintech company gathers data, which creates digital identity management and data ownership concerns. But what happens to a customer’s data after they’ve canceled a subscription? Data deletion mechanisms, therefore, need to be in place, the absence of which can cause compliance issues and data stealing by attackers. This takes us to the next pain point of cybersecurity, i.e., data security.
- Data Security- $18.5 million approximately! That is the annual cost spent by capital market firms and banks on combating cybercrimes, underscores the Accenture study. Hackers target system weaknesses to exploit information like financial data, contact, and personally identifiable information. 64% of the fintech companies are aware of such data breaches only until it’s too late.
- Regional Security Requirements- Fintech companies must follow regulations concerning regional data protection and KYC (Know Your Customer) practices. Privacy legislation at a regional level limits FinTech software on the data that it can collect and process. Fintech companies also need to make an understanding of how different countries can interpret the same legislative concepts. FinTech apps therefore must be built with practical tools and an understanding of the local regulations. In the absence of this, a FinTech company may isolate itself from certain markets.
Apart from the aforementioned challenges, Deloitte mentions the following challenges in managing cybersecurity as well (Fig. 2).

But, what are the factors or underlying reasons that can cause such security threats as far as cybersecurity and data protection are concerned?
Factors attributing to cybersecurity threats
A lot of attacks mentioned above are caused due to factors like:
- Inadequate security on devices of end-users
- Unpatched and vulnerable operating systems
- Installing cracked applications on devices
- Incomprehensive designing of security controls for products that digital payment products
- API exposure to untrusted and untested interfaces due to multiple data interface across product
All the aforementioned challenges can be tackled with the software development vendor and engineering partner who understands these concerns in and out. Valuebound has helped FinTech companies worldwide in building secure products with careful methodologies and frameworks. We suggest following FinTech cybersecurity solutions to make your platform safer and secure.
Cybersecurity Solutions for FinTech Companies
Companies that give due importance to financial well-being and brand value must also leverage the latest data security techniques and methodologies. What can a FinTech company do for data protection and cybersecurity?
Let’s consider some of the industry best practices for building FinTech products with robust security.
Data Encryption
Encryption is a process of encoding critical information into codes that need special keys for deciphering it in an understandable and readable format. FinTech companies can secure data with complex technologies and encryption algorithms like RSA (highly secure algorithm with private and public encryption keys), Twofish (freeware algorithm encrypting data into 128-bit blocks), 3DES (encryption method preferred for credit card PINs encryption), P2PE and EMV.
“Technologies that devalue data such as– Tokenization, P2PE, EMV & 3DS can play a critical role in helping prevent theft incidents from becoming breaches,” says Nitin Bhatnagar, Associate Director, India, PCI SSC. The goal behind data encryption is the elimination of persistent value in data that is used to perform a transaction. Hence, if an attacker tries to steal information or data, the merchant, consumer, and system still remain secure.
Tokenization
The process of replacing sensitive information with a generated number or token is called tokenization. Unique databases or token vaults may be used to decrypt original data into readable formats. To make a FinTech app even more secure, companies can also encrypt a token vault.
Today, tokenization has emerged as a real game changer, especially in the payments ecosystem. It must be adopted to ensure payment security, improve payment data security, and also address consumer privacy concerns.
Role-Based Access Control
A FinTech app typically can include the roles of an IT Specialist, admin, manager, support staff and the customer. Role based access control (RBAC) can then be used to restrict access to a network depending upon the user’s association with the FinTech company. This ensures restricted or varying access or regular employees and end-users who then cannot use corporate information. Conclusively, it reduces security threats, both internally as well as externally. RBAC-enabled product development requires solid engineering capabilities and robust technical expertise.
Implementing Authentication Technologies
One-Time Passwords (OTPs), mandatory change of passwords, monitoring suspicious activities like failed logins, short log-in sessions, and multi-factor authentication are some of the authentication methodologies that help in securing data by understanding and analyzing user behavior. Dynamix extra layers of protection can help users in completing their transactions safely and securely.
DevSecOps
DevOps is the common practice among most software development companies, but now with cybersecurity being at the core of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), DevSecOps has become the new vogue. What’s the difference? DevSecOps means the prioritization of developing a secure codebase with the same DevOps principles, i.e., CI/CD (Continuous Integration/ Continuous Development), collaboration, automation, and communication. DevSecOps only shifts its focus on embedding security at the early stages of SDLC. DevSecOps methodology uses cybersecurity at the central part of the production pipeline with other phases like architectural designing, coding, and testing.
Building secure FinTech products and solutions
The average data breach costs in 2021 is $4.24 million, a 10% rise from 2020 findings, according to IBM and Ponemon Institute report, and the most common initial attack vector is compromised credentials. This speaks volumes about the concerns of FinTech companies in developing a secure FinTech solution. So how do you plan to build a secure app with limited resources? Valuebound’s product engineering team builds a secure platform and high-grade product with all regulations and security concerns under consideration.
Our team sprints with clients to create a validated hypothesis with a security roadmap, analysis and risk log, cloud assessment, AWS Security Maturity document, and budget. If you wish to develop a secure FinTech solution or have a compliant concern, speak to us to learn more about our software development and product engineering services for FinTech cybersecurity.





