Understanding async-await in Javascript
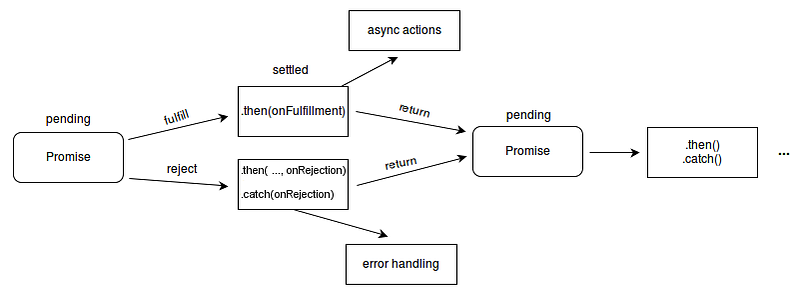
Async and Await are extensions of promises. So if you are not clear about the basics of promises please get comfortable with promises before reading further. You can read my post on Understanding Promises in Javascript.
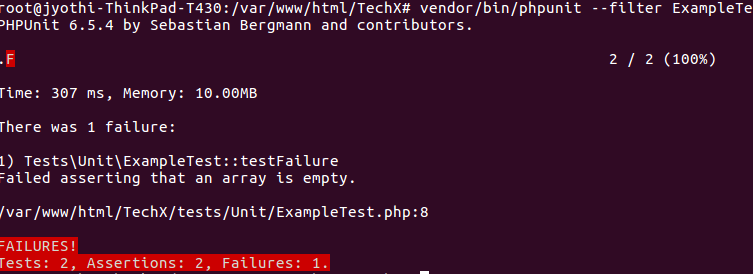
I am sure that many of you would be using async and await already. But I think it deserves a little more attention. Here is a small test : If you can’t spot the problem with the below code then read on.
for (name of ["nkgokul", "BrendanEich", "gaearon"]) {
userDetails = await fetch("https://api.github.com/users/" + name);
userDetailsJSON = await userDetails.json();
console.log("userDetailsJSON", userDetailsJSON);
}
We will revisit the above code block later, once we have gone through async await basics. Like always Mozilla docs is your friend. Especially checkout the definitions.
async and await
From MDN
An asynchronous function is a function which operates asynchronously via the event loop, using an implicit Promise to return its result. But the syntax and structure of your code using async functions is much more like using standard synchronous functions.
I wonder who writes these descriptions. They are so concise and well articulated. To break it down.
- The function operates asynchronously via event loop.
- It uses an implicit Promise to return the result.
- The syntax and structure of the code is similar to writing synchronous functions.
And MDN goes on to say
Anasyncfunction can contain anawaitexpression that pauses the execution of the async function and waits for the passedPromise's resolution, and then resumes theasyncfunction's execution and returns the resolved value. Remember, theawaitkeyword is only valid insideasyncfunctions.
Let us jump into code to understand this better. We will reuse the three function we used for understanding promises here as well.
A function that returns a promise which resolves or rejects after n number of seconds.
var promiseTRRARNOSG = (promiseThatResolvesRandomlyAfterRandomNumnberOfSecondsGenerator = function() {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
let randomNumberOfSeconds = getRandomNumber(2, 10);
setTimeout(function() {
let randomiseResolving = getRandomNumber(1, 10);
if (randomiseResolving > 5) {
resolve({
randomNumberOfSeconds: randomNumberOfSeconds,
randomiseResolving: randomiseResolving
});
} else {
reject({
randomNumberOfSeconds: randomNumberOfSeconds,
randomiseResolving: randomiseResolving
});
}
}, randomNumberOfSeconds * 1000);
});
});
Two more deterministic functions one which resolve after n seconds and another which rejects after n seconds.
var promiseTRSANSG = (promiseThatResolvesAfterNSecondsGenerator = function(
n = 0
) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
resolve({
resolvedAfterNSeconds: n
});
}, n * 1000);
});
});
var promiseTRJANSG = (promiseThatRejectsAfterNSecondsGenerator = function(
n = 0
) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
reject({
rejectedAfterNSeconds: n
});
}, n * 1000);
});
});
Since all these three functions are returning promises we can also call these functions as asynchronous functions. See we wrote asyn functions even before knowing about them.
If we had to use the function promiseTRSANSG using standard format of promises we would have written something like this.
var promise1 = promiseTRSANSG(3);
promise1.then(function(result) {
console.log(result);
});
promise1.catch(function(reason) {
console.log(reason);
});
There is a lot of unnecessary code here like anonymous function just for assigning the handlers. What async await does is it improves the syntax for this which would make seem more like synchronous code. If we had to the same as above in async await format it would be like
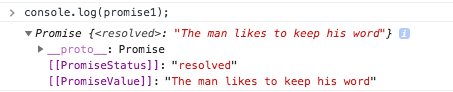
result = await promiseTRSANSG(3); console.log(result);
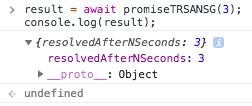
Well that look much more readable than the standard promise syntax. When we used await the execution of the code was blocked. That is the reason that you had the value of the promise resolution in the variable result. As you can make out from the above code sample, instead of the .then part the result is assigned to the variable directly when you use await You can also make out that the .catch part is not present here. That is because that is handled using try catch error handling. So instead of using promiseTRSANSlet us use promiseTRRARNOSG Since this function can either resolve or reject we need to handle both the scenarios. In the above code we just wrote two lines to give you an easy comparison between the standard format and async await format. The example in next section gives you a better idea of the format and structure.
General syntax of using async await
async function testAsync() {
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
result1 = await promiseTRRARNOSG();
console.log("Result 1 ", result1);
result2 = await promiseTRRARNOSG();
console.log("Result 2 ", result2);
} catch (e) {
console.log("Error", e);
} finally {
console.log("This is done");
}
}
}
test();
From the above code example you can make out that instead of using the promise specific error handling we are using the more generic approach of using try catch for error handling. So that is one thing less for us to remember and it also improves the overall readability even after considering the try catch block around our code. So based on the level of error handling you need you can add any number of catch blocks and make the error messages more specific and meaningful.
Pitfalls of using async and await
async await makes it much more easier to use promises. Developers from synchronous programming background will feel at home while using asyncand await. This should also alert us, as this also means that we are moving towards a more synchronous approach if we don’t keep a watch.
The whole point of javascript/nodejs is to think asynchronous by default and not an after though. async await generally means you are doing things in sequential way. So make a conscious decision whenever you want to use to async await.
Now let us start analysing the code that I flashed at your face in the beginning.
for (name of ["nkgokul", "BrendanEich", "gaearon"]) {
userDetails = await fetch("https://api.github.com/users/" + name);
userDetailsJSON = await userDetails.json();
console.log("userDetailsJSON", userDetailsJSON);
}
This seems like a harmless piece of code that fetches the github details of three users “nkgokul”, “BrendanEich”, “gaearon” Right. That is true. That is what this function does. But it also has some unintended consequences.
Before diving further into the code let us build a simple timer.
startTime = performance.now(); //Run at the beginning of the code
function executingAt() {
return (performance.now() - startTime) / 1000;
}
Now we can use executingAt wherever we want to print the number of seconds that have surpassed since the beginning.
async function fetchUserDetailsWithStats() {
i = 0;
for (name of ["nkgokul", "BrendanEich", "gaearon"]) {
i++;
console.log("Starting API call " + i + " at " + executingAt());
userDetails = await fetch("https://api.github.com/users/" + name);
userDetailsJSON = await userDetails.json();
console.log("Finished API call " + i + "at " + executingAt());
console.log("userDetailsJSON", userDetailsJSON);
}
}
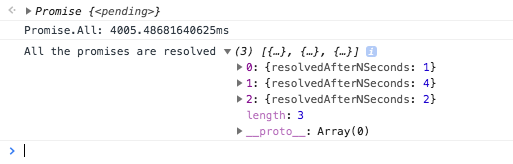
Checkout the output of the same.
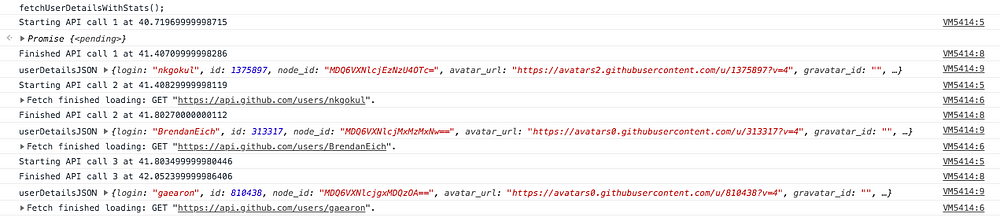
As you can find from the output, each of the await function is called after the previous function was completed. We are trying to fetch the details of three different users“nkgokul”, “BrendanEich”, “gaearon” It is pretty obvious that output of one API call is in noway dependent on the output of the others.
The only dependence we have is these two lines of code.
userDetails = await fetch("https://api.github.com/users/" + name);
userDetailsJSON = await userDetails.json();
We can create the userDetailsJSON object only after getting the userDetails. Hence it makes sense to use await here that is within the scope of getting the details of a single user. So let us make an async for getting the details of the single user.
async function fetchSingleUsersDetailsWithStats(name) {
console.log("Starting API call for " + name + " at " + executingAt());
userDetails = await fetch("https://api.github.com/users/" + name);
userDetailsJSON = await userDetails.json();
console.log("Finished API call for " + name + " at " + executingAt());
return userDetailsJSON;
}
Now that the fetchSingleUsersDetailsWithStats is async we can use this function to fetch the details of the different users in parallel.
async function fetchAllUsersDetailsParallelyWithStats() {
let singleUsersDetailsPromises = [];
for (name of ["nkgokul", "BrendanEich", "gaearon"]) {
let promise = fetchSingleUsersDetailsWithStats(name);
console.log(
"Created Promise for API call of " + name + " at " + executingAt()
);
singleUsersDetailsPromises.push(promise);
}
console.log("Finished adding all promises at " + executingAt());
let allUsersDetails = await Promise.all(singleUsersDetailsPromises);
console.log("Got the results for all promises at " + executingAt());
console.log(allUsersDetails);
}
When you want to run things in parallel, the thumb rule that I follow is
Create a promise for each async call. Add all the promises to an array. Then pass the promises array to Promise.all This in turn returns a single promise for which we can use await
When we put all of this together we get
startTime = performance.now();
async function fetchAllUsersDetailsParallelyWithStats() {
let singleUsersDetailsPromises = [];
for (name of ["nkgokul", "BrendanEich", "gaearon"]) {
let promise = fetchSingleUsersDetailsWithStats(name);
console.log(
"Created Promise for API call of " + name + " at " + executingAt()
);
singleUsersDetailsPromises.push(promise);
}
console.log("Finished adding all promises at " + executingAt());
let allUsersDetails = await Promise.all(singleUsersDetailsPromises);
console.log("Got the results for all promises at " + executingAt());
console.log(allUsersDetails);
}
async function fetchSingleUsersDetailsWithStats(name) {
console.log("Starting API call for " + name + " at " + executingAt());
userDetails = await fetch("https://api.github.com/users/" + name);
userDetailsJSON = await userDetails.json();
console.log("Finished API call for " + name + " at " + executingAt());
return userDetailsJSON;
}
fetchAllUsersDetailsParallelyWithStats();
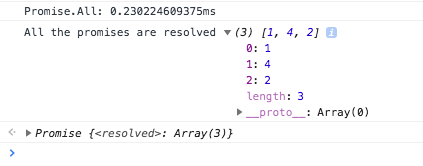
The output for this is
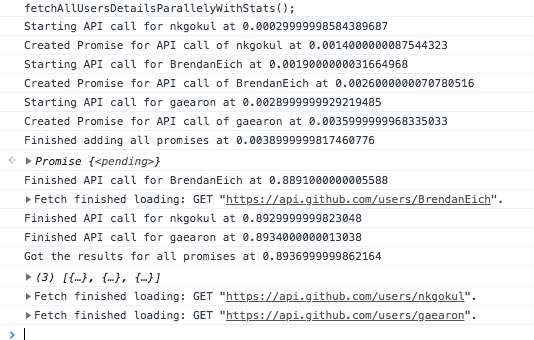
As you can make out from the output, promise creations are almost instantaneous whereas API calls take some time. We need to stress this as time taken for promises creation and processing is trivial when compared to IO operations. So while choosing a promise library it makes more sense to choose a library that is feature rich and has better dev experience. Since we are using Promise.all all the API calls were run in parallel. Each API is taking almost 0.88 seconds. But since they are called in parallel we were able to get the results of all API calls in 0.89 seconds.
In most of the scenarios understanding this much should serve us well. You can skip to Thumb Rules section. But if you want to dig deeper read on.
Digging deeper into await
For this let us pretty much limit ourselves to promiseTRSANSG function. The outcome of this function is more deterministic and will help us identify the differences.
Sequential Execution
startTime = performance.now();
var sequential = async function() {
console.log(executingAt());
const resolveAfter3seconds = await promiseTRSANSG(3);
console.log("resolveAfter3seconds", resolveAfter3seconds);
console.log(executingAt());
const resolveAfter4seconds = await promiseTRSANSG(4);
console.log("resolveAfter4seconds", resolveAfter4seconds);
end = executingAt();
console.log(end);
}
sequential();
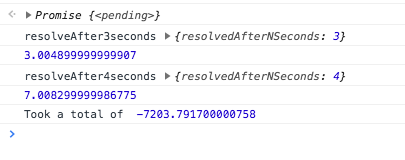
Parallel Execution using Promise.all
var parallel = async function() {
startTime = performance.now();
promisesArray = [];
console.log(executingAt());
promisesArray.push(promiseTRSANSG(3));
promisesArray.push(promiseTRSANSG(4));
result = await Promise.all(promisesArray);
console.log(result);
console.log(executingAt());
}
parallel();
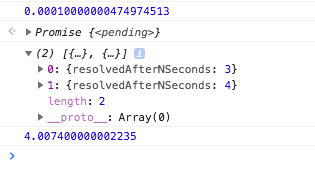
Concurrent Start of Execution
asynchronous execution starts as soon as the promise is created. await just blocks the code within the async function until the promise is resolved. Let us create a function which will help us clearly understand this.
var concurrent = async function() {
startTime = performance.now();
const resolveAfter3seconds = promiseTRSANSG(3);
console.log("Promise for resolveAfter3seconds created at ", executingAt());
const resolveAfter4seconds = promiseTRSANSG(4);
console.log("Promise for resolveAfter4seconds created at ", executingAt());
resolveAfter3seconds.then(function(){
console.log("resolveAfter3seconds resolved at ", executingAt());
});
resolveAfter4seconds.then(function(){
console.log("resolveAfter4seconds resolved at ", executingAt());
});
console.log(await resolveAfter4seconds);
console.log("await resolveAfter4seconds executed at ", executingAt());
console.log(await resolveAfter3seconds);
console.log("await resolveAfter3seconds executed at ", executingAt());
}; concurrent();
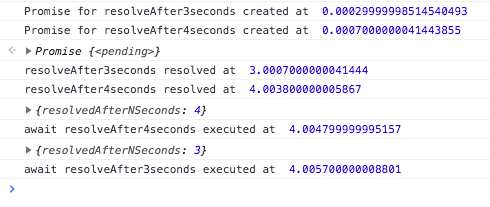
From previous post we know that .then is even driven. That is .then is executed as soon as the promise is resolved. So let us use resolveAfter3seconds.thenand resolveAfter4seconds.then to identify when our promises are actually resolved. From the output we can see that resolveAfter3seconds is resolved after 3 seconds and resolveAfter4secondsis executed after 4 seconds. This is as expected.
Now to check how await affects the execution of code we have used
console.log(await resolveAfter4seconds); console.log(await resolveAfter3seconds);
As we have seen from the output of .then resolveAfter3seconds resolved one second before resolveAfter4seconds . But we have the await for resolveAfter4seconds and then followed by await for resolveAfter3seconds
From the output we can see that though resolveAfter3seconds was already resolved it got printed only after the output of console.log(await resolveAfter4seconds); was printed. Which reiterates what we had said earlier. await only blocks the execution of next lines of code in asyncfunction and doesn’t affect the promise execution.
Disclaimer
MDN documentation mentions that Promise.all is still serial and using .then is truly parallel. I have not been able to understand the difference and would love to hear back if anybody has figured out their heard around the difference.
Thumb Rules
Here are a list of thumb rules I use to keep my head sane around using asyncand await
ayncfunctions returns a promise.asyncfunctions use an implicit Promise to return its result. Even if you don’t return a promise explicitlyasyncfunction makes sure that your code is passed through a promise.awaitblocks the code execution within theasyncfunction, of which it(await statement) is a part.- There can be multiple
awaitstatements within a singleasyncfunction. - When using
async awaitmake sure to usetry catchfor error handling. - If your code contains blocking code it is better to make it an
asyncfunction. By doing this you are making sure that somebody else can use your function asynchronously. - By making async functions out of blocking code, you are enabling the user who will call your function to decide on the level of asynhronicity he wants.
- Be extra careful when using
awaitwithin loops and iterators. You might fall into the trap of writing sequentially executing code when it could have been easily done in parallel. awaitis always for a single promise. If you want toawaitmultiple promises(Run this promises in parallel) create an array of promises and then pass it to thePromise.allfunction.- Promise creation starts the execution of asynchronous functionality.
awaitonly blocks the code execution within theasyncfunction. It only makes sure that next line is executed when thepromiseresolves. So if an asynchronous activity has already started thenawaitwill not have an effect on it.
Please point out if I am missing something here or if something can be improved.
Originally published on https://hackernoon.com/understanding-async-await-in-javascript-1d81bb07…