Gatsby and Drupal : Match made in heaven?
Gatsby is a popular static site generator that can communicate with any backend.
The front-end landscape has exploded in the last three years. Today you have various libraries/front end frameworks like React, Angular, VueJS. You have tightly coupled full stack frameworks NEXT, NUXT etc. Of all these options Gatsby finds a sweet spot with its JAM stack approach. JAMstack is “a modern web development architecture based on client-side JavaScript, reusable APIs, and prebuilt Markup.”
In this article we will discuss how we can make use of the JAM stack using Gatsby and Drupal. We will also cover the general questions that are generally not answered in the blogs.
- Gatsby is static site generator, so what are the scenarios where I can use Gatsby.
- My site has a lot of dynamic content, how do I make it work well with Gatsby.
- I have read that Gatsby is based on React, so how can I decide when to use Gatsby and when to use React only front end.
- Can I use gatsby to progressive decouple my Drupal website?
- How can I configure Gatsby so that most of the configurations are read from the backend and a parity is maintained with current existing website.
- What is server side rendering and how can I leverage it with my Gatsby and Drupal set up.
- Is Gatsby good only for the anonymous user or can I leverage it for authenticated flows as well?
- Setting up OAuth on Drupal and leveraging the same for Gatsby.
- What is the relationship between jsonapi and graphql.
- Setting up Gatsby
- What are the other alternatives that play well with Drupal.
- Should I use Gatsby or Tome?
- Feedback
There are many todo articles that already explain how to get started with Drupal and Gatsby. I will just link to them here instead of repeating and answer the questions that I had when following them. If you have already made your decision just visit the Setting up Gatsby section.
What is JAM stack
JAMstack is “a modern web development architecture based on client-side JavaScript, reusable APIs, and prebuilt Markup.” In a crude analogy you can think of it like the static files deployment that you were doing if you were in software development say a decade ago. This is not entirely true but JAM stack tries to combine the ease of static sites along with the dynamicness provided by APIs.
Javascript : Javascript is used for the client side interactions, better handling of dynamic rendering of elements on the client side and also for interaction with the backend if any. Think AJAX.
APIS : Any interaction with the backend is abstracted into reusable APIs. One more advantage is that in the front end you can make use of your own APIs as well as any third party APIs.
Markup : You will using the Markup or HTML/css for the front end. In JAM stack markup is generally prebuilt at the deploy time.
Gatsby is static site generator, so what are the scenarios where I can use Gatsby?
Gatsby is a static site generator. What this means is that the public folder that is created during the build time will function as a static website. So you can take that folder and deploy it on any server with Apache or nginx like server to serve the requests. For example if you use the default starter kit of Gatsby communicating with Drupal backend, you only need the backend to be up during the build time. Once your build is done, you can down your Drupal server and just deploy the public folder generated during the build. What this means is that your Gatsby site will communicate with your Drupal backend during the build time, fetch all the details necessary and create static files for all the paths that will be present on your site.
My site has a lot of dynamic content, how do I make it work well with Gatsby.
Think of Gatsby as a state-machine. The state consists of the code changes you make and also the data you save in your database. So whenever there is a change in the code or the data in the database, you need to rebuild it for the latest state. For code changes it is easier to trigger the build. For the changes in database it is a little bit difficult. But you can make use of web hooks to trigger these builds. But the question is how frequently do you trigger your builds? Let us say that you can stay with some stale data, then you can have builds every few hours. This might be suitable for blogs where if the content is refreshed every couple of hours/days it should be sufficient. But if your site has lot of user interactions then frequent rebuilds might be a pain and it will also add load on the server. In such scenarios it would make sense to keep the content that changes less frequently in a backend like Drupal and for the content that changes frequently(like comments) it might be better to off load to a third party service(like Disqus for comments).
I have read that Gatsby is based on React, so how can I decide when to use Gatsby and when to use React only front end.
If you would like to have control of all your data(both that changes less frequently and more frequently) then it might make sense to do the Gatsby build for content that changes less frequently, then add React components that interact with live API calls for content that changes more frequently. Since Gatsby is built on React, you can stick to your standard API calls in componenentDidMount and then render the results in render function.
Can I use gatsby to progressive decouple my Drupal website?
If you are not sure whether to use Gatsby for the whole of your site, then this approach can be good. For example let us say that you have a website that has many functionalities including blog, you can just transfer the client facing blog functionality of your website to Gatsby. In your apache/nginx config just make sure that only example.com/blog is handled by your Gatsby front end and all other parts are handled by Drupal.
How can I configure Gatsby so that most of the configurations are read from the backend and parity is maintained with the current existing website?
One simple approach I took was to make sure that I have Drupal backend at backend.example.com and front end at gatsby.example.com
In my gatsby-node.js I added a rule like
result.data.allNodePage.edges.forEach(({ node }) => {
createPage({
path: node.path.alias,
component: staticPageTemplate,
context: {
slug: node.path.alias,
},
})
})
This makes sure that even in the gatsby front end I can use the path set in the backend. So for example backend.example.com/blog/firstblog to gatsby.example.com/blog/firstblog This way it was easier for me to map and check the missing pages from the sitemap.xml as well.
What is server-side rendering and how can I leverage it with my Gatsby and Drupal set up.
Gatsby comes with a default SSR settings. What it means is that API calls to your data sources are made at the build time. So all the pages are server side rendered. Once you are done with a build you can pretty much shut down your backend unless you have any real time API calls that you need to do from your Gatsby app.
Is Gatsby good only for the anonymous user or can I leverage it for authenticated flows as well?
By default Gatsby plays well for read only kind of websites. But there is nothing that stops you from creating forms and authenticated user flows as it internally used React. Connecting Gatsby with Redux might be good for authenticated flows. Checkout https://medium.freecodecamp.org/how-to-get-started-with-gatsby-2-and-redux-ae1c543571ca for Gatsby with Reduct integration. If you want to add authentication to your Gatsby sites checkout https://www.gatsbyjs.org/blog/2019-03-21-add-auth0-to-gatsby-livestream/#authentication-in-gatsby
What is the relationship between jsonapi and graphql.
In Drupal jsonapi is a popular module. There is also a graphql module. But if you are using https://www.gatsbyjs.org/packages/gatsby-source-drupal/ plugin you will observe that on the Drupal end you just enable the jsonapi module thats all. What is happening is that the the GatsbySourceDrupal plugin is taking care of the jsonapi output and converting it to graphql compliant structure so that you can actually use graphql queries to access your data in Drupal. You are generally asked to enable the jsonapi access to all user. Be careful as you might be exposing some confidential data that is not intended. Do check these out before deploying in live.
What are the other alternatives that play well with Drupal?
Gatsby is a great tool. It makes starting with REACT and Drupal so easy. It is also highly configurable and customizable. But it can still be overwhelming for Drupal developers who have not worked with Frontend frameworks earlier. Thanks to open source we have other alternatives.
Tome is another interesting project that generates static sites for Drupal 8 quickly and without needing to know the new frontend libraries and tools.
In https://twitter.com/DrupalSAM’s own words
It’s important for me to make Tome more accessible to less technical users. Anyone that can make a Drupal site should be able to make a static site without learning a completely different toolset and programming language.
I think this is a great goal and will help the Drupal community immensely. Once people realize the advantage of JAM architecture I am sure most of the blog like sites will default to static sites :)
If you don’t trust me, just check out the video in below tweet to realize how easy it is to create static sites with Tome.
https://twitter.com/DrupalSAM/status/1091813197214928896
Should I use Gatsby or Tome?
As with most answers to the technical questions, that answer is “It depends” :P
But here is the thumb rule I use.
- If you are not comfortable with Frontend and you just want to use JAM stack or static sites for the performance sake Tome is a great choice. There is not much addition learning curve.
- If you want to leverage the fast pace of development in REACT eco-system but don’t want to build things from scratch, you can leverage Gatsby.
Setting up Gatsby
Before setting up Gatsby I would recommend going through the following two videos. They give you a high level insights and should be sufficient to get you started quickly.
1. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PKMTLyIpbvQ
Understanding Gatsby Internals for Drupal
If you would like to understand the details of how Gatsby works and how to customise it for Drupal, you can check out this blog by Ryan Bateman
Tutorial: GatsbyJS for Drupalers; or, How to JAMStack-ify your Drupal Site with GatsbyJS
GatsbyJS is everywhere these days. The upstart react-based site generator has come a long way from its humble…www.ryanbateman.space
Things I wish I knew in Gatsby before getting started
- Gatsby also uses the term node. This is different from the node used in Drupal.
- Any atomic data that Gatsby handles can be considered as node. So in Gatsby lingo Drupal nodes, categories, taxonomy terms and users can also be considered as nodes.
- There is no rule that each Gatsby node needs to have a page. You can decide for which nodes you need to create pages.
Feedback
I hope this answers some of your questions before shifting to Decoupled Drupal site or deciding on the front end frameworks for your Drupal API backend. I have collected all these highlights and notes about Drupal/Gatsy using our extension. Once you do that, you can search all your notes from our dashboard.
If you have any questions that I am not able to answer just let me know about them in comments. We can explore them together and share our notes for mutual benefit. Let us make this as a repository for all the commonly asked Questions by Drupallers regarding headless option.
Why I am finally switching from chrome to Brave
TLDR : Brave is fast, secure and a cryptocurrency driven (for marketing and fixing the ad model of web) browser. It is trying to fix the internet as we know today, by improving the ad model. Having known about it couple of months ago, I had been postponing my switch to Brave for lack of extensions support. Now they have started supporting chrome extensions and hence I am switching.
The Long Version
The thing with tools is that once you choose one and get used to it, it is really difficult to replace them. This is true even if the new alternative is much better than the old one. With the rapid pace of development today there is a tough competition and a close fight most of the times. With nightly builds and weekly releases, it is too taxing to compare the strengths of tools objectively on a regular basis. When was the last time you even considered an alternative browser. Do you compare the latest features of the popular browser every month? at-least once in every quarter? How about every six months? Well yes. Not many people do. I didn’t either. It is very rare that we go back to drawing room to review and decide what tools to use on a regular basis. It is too much of work. So we make the decision and stick to it until we are forced to change. We know that is not ideal but that is how we are all wired I guess. I am saying all this because inspite of all these I am switching to Brave and you might go through the same when you consider it ;)
Who is behind Brave
I first heard about this project almost an year ago during its ICO. I was curious about this project as it was co-founded by the Brendan Eich. He is best known as the creator of the ubiquitous Javascript programming language. He was also a co-founder of Mozilla, the organisation behind the open-source web browser Firefox. In addition to Brendan Eich the team has some great names with each of them being a pro in one critical feature of the project. Go checkout https://basicattentiontoken.org/about/ in details once you are done reading this article and you will know what I mean.

With such a great line up, people would definitely take note when the team speaks. In fact they have they have been making use of this quite effectively.
Features of the browser
If I had to put down the features of this browser in the order I like them the most it would be.
- Browse Faster
- Protect your Privacy — Blocks trackers.
- Httpseverywhere.
- TOR integration.
- Block Ads by default.
- Fixing the Ad model — Pay your favourite publishers.
- Marketing
- Chrome extensions support.
Browse Faster
Their website claims that the browser is upto 2 times faster on desktop and upto 8 times faster on mobile. I have not “run my horses” yet, but even during the normal usage I could see that the browser was way faster compared to other browsers. The browser start time is also very less. Personally this is critical for me. Couple of years ago though I liked everything else about Firefox I didn’t move to it, as it used to take very long for a cold start.
Protect your Privacy — Blocks trackers
I have been using this browser for only couple of minutes now and I can already see that it has blocked 129 trackers. I was really blind to the fact that there were so many trackers tracking me on every popular site I visit. I am a little more confident now that my personal data and patterns will not be sold to marketers without my consent. Brave did a good job of keeping track of these numbers and showing them visually on the browser. This will definitely raise the awareness.
https everywhere
This is more of a misnomer. I thought this would automatically convert all http sites to https sites. That is create a secure channel on the go. How foolish of me :P If the certificate is not installed on the server and website has not enabled https, I don’t think there is much the browser can do. But looks like I am not the only as I read couple of discussions regarding this where people assumed that “https upgrades” it will create secure channels. But looks it only means redirections when https version is available.
https upgrades means, sites and hyperlinks, that are linked to http:// and if a equivalent https:// site is available… brave browser, automatically changes those links to https:// equivalents, to prevent tracking etc.,
I think brave should rephrase this as it can be misleading. If you have not yet decided to use brave you can use the httpseverywhere extension. After having realised what “httpseverywhere” it is no more a killer feature I thought it was. But I am leaving it here in this position, as many people might misunderstand it like I did.
TOR Integration
Though I have read couple of times about TOR I have never really found the need to need to use them. While that is one of the reasons, the other is that I am lazy. But looks like Brave is making using TOR very easy.
When you open a new private tab brave shows this message. Now you can start using TOR with a private browser. Isn’t that cool?
You can start a new private tab with TOR, by doing a right click on the new tab icon in any one of the existing tabs.
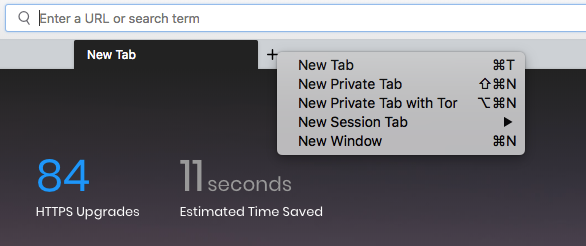
The documentation is not clear about how to open a “New Private Tab with Tor”. I think Brave should change the message on the first screen so that people have clear instructions about using this feature.
Blocks ads by default
I have never used ad blockers until recently. Having managed a couple of small websites in the past, I realise the issues of the publishers. If most users start using “ad blockers” then the publishers will have to find alternative sources of income. Since there were none, I never felt using Ad blockers. But now Brave is coming out with a very good solution for this problem, which we will discuss later.
However while going through the brave download page I came across a new information that was surprising. We never realize that we might be paying substantial amount to ISPs for downloading ads and trackers which we don’t want. So I was naturally surprised to find out the actual figures. Brave claims that it is $276 for an year.
The average mobile browser user pays as much as $23 a month in data charges to download ads and trackers — that’s $276 a year. Brave blocks ads and trackers, so you don’t pay for them.
Now that brave has an alternative revenue model I think we can safely start using “Disable ads and trackers”.
Timing
You can get everything else right but if your timing is wrong there is nothing much you can do. We all know of many of our favourite projects which got everything right but failed to get mass adoption just because they were either ahead of time or they were late. So timing is very critical.
I think brave is entering the markets in the right time. Following are couple of reasons I think that timing is right.
- Facebook sells personal data — http://fortune.com/2018/04/10/facebook-cambridge-analytica-what-happened/
- Google might face record fine in Android monopoly case — https://www.expresscomputer.in/news/google-might-face-record-fine-in-android-monopoly-case/25864/
- 50 millions Facebook accounts might be compromised — https://www.cnbc.com/2018/10/02/facebooks-muddy-account-breach-response-could-be-the-new-norm.html
- Time Berners Lee starts Solid — A web where the users have complete control over their data. https://medium.com/@timberners_lee/one-small-step-for-the-web-87f92217d085
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies are here to stay (Brave is using them. Read in the next sections below) — https://www.finpipe.com/why-blockchain-is-here-to-stay-2/
Revenue Model
Digital advertising is broken and online publishing is dying a slow death. These are interrelated and one cannot be fixed without fixing the other. In the words of founders of Brave “It is a market filled with middlemen and fraudsters, hurting users, publishers and advertisers.”
The Basic Attention Token (BAT) was developed to address this. BAT, an ERC20token built on top of Ethereum, will be the token of utility in a new, decentralized, open source and efficient blockchain-based digital advertising platform.
In the ecosystem, advertisers will give publishers BATs based on the measured attention of users. Users will also receive some BATs for participating. They can donate them back to publishers or use them on the platform.
This transparent system keeps user data private while delivering fewer but more relevant ads. Publishers experience less fraud while increasing their percentage of rewards. And advertisers get better reporting and performance.
The following revenue split seems to be fair enough and looks it is taking everybody’s interest into consideration.
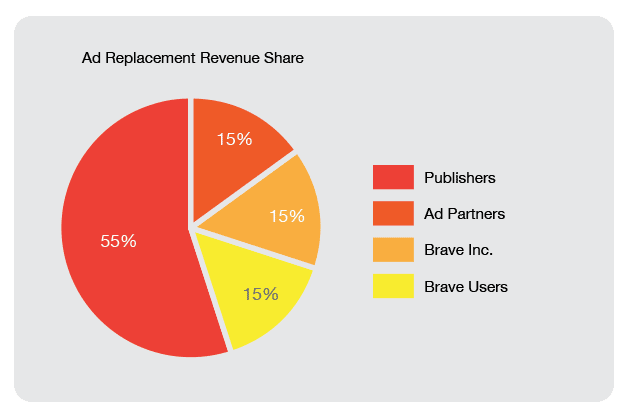
The best part is that Brave is not forcing anything upon the users. Based on your preference you can choose any of the paths below.
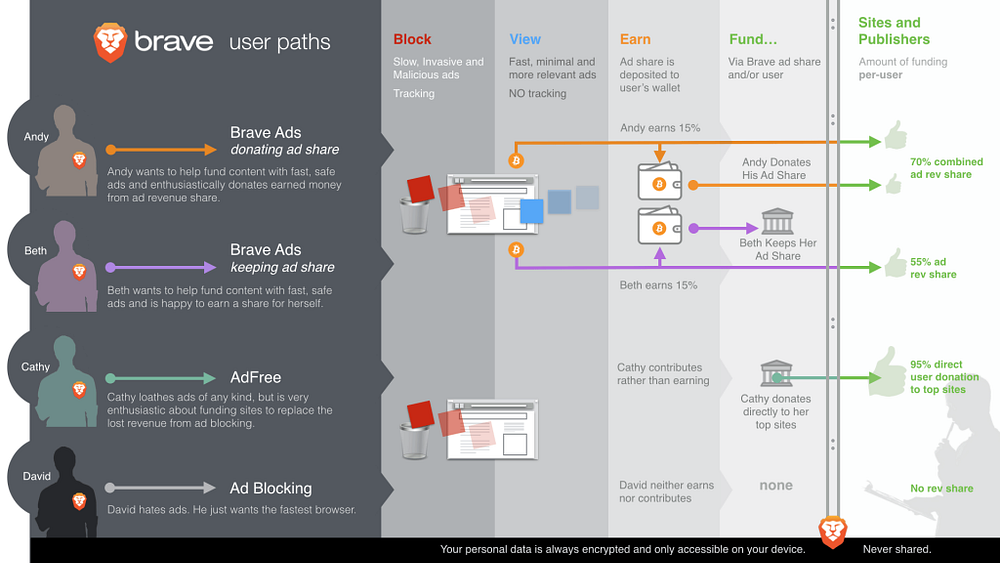
It is heartening to see that Brendan and team are not going for token liquidation are privately funded. This shows their commitment in the product for the long term. Not everybody can have this luxury. But it definitely boosts confidence to know that they are thinking long term. Browsers will take time for adoption and having deep Marketing
Best viewed with Chrome or Firefox
We have all see the following message on various websites couple of years ago. Developers liked these browsers as it was easier to code front end of websites for these browsers. Naturally most of the websites started promoting these browsers as well.
But their association with the browsers pretty much ended there. With Brave the scenario changes. Since the publishers can get paid for their efforts and content, they have a vested interest to promote the browser. Whether the revenues from this source will be sufficient to replace the revenues from ads is something that we need to wait and watch. But it can already be considered as an alternative source of income.
Marketing Budget
While there are examples of open source projects like Linux, Apache etc gaining popularity even without much of marketing, marketing is critical especially for a browser to gain traction. Looks like Brave it not shying here. They are spending real dollars on customer acquisition.
5 USD Custom Acquisition Cost
For every active user converted, I think Brave is paying close to 5USD. Not many publishers might depend on this. But for the new model to gain adoption and challenge the big wigs like chrome and Firefox, the number of users using this browser should definitely sky rocket. When the product is good, don’t underestimate the power of referrals. We all are aware of how Paypal referrals snowballed and made it a house hold name in a very short span of time. Don’t be surprise if the same happens to Brave browser.
I just added the following banner on my website bakkt.com/blog/company/introducing-bakktom/blog/company/introducing-bakkt

You will start seeing images like below very soon on many publications going forward. Get used to it. Online publishing industry have been dying a slow death. Everybody is looking for a way out, but nobody is able to figure out a model that is a win-win for the reader and publisher. If Brave can do that I am sure that most of the publications will flock to this model. But again it will all come down to crossing the critical mass. It is good that Brave is privately funded and they seem to be ready to burn money until they cross 15 Million Monthly Active Users.
Positioning
Brave is trying to position itself as the privacy centric browser. Google’s chrome which was the David against the Goliath(Internet Explorer) has now become the new Goliath and Brave is positioning itself as the new David. Recently Brave filed a privacy complaint against Google. This could be huge if Google lands up on the wrong side of the verdict. It will not only help Brave garner the much required publicity but it will also help cement its position as privacy centric browser and representative of the common man against the monopoly of Google which could play well for Brave over the coming years.
Support for chrome extension
Regarding moving to chromium base the blog says
Which we believe will allow us to focus more fully on Brave features and less on Chromium upgrades and basic browser work.
I think this is a brilliant strategy. Google is doing a great job of making chrome fast and cutting edge. The problem with chrome has been with respect to the overreaching control it will have once we start using their browser. So this approach of Brave is a master stroke I would say.
If you want to give the latest version a try you can checkout the brave dev version.

Since the dev version uses the chromium it also means that the chrome extensions are now supported. I installed a couple of extensions to check them out and they are functioning without any issues. This was a major hold back and now I have moved to Brave.
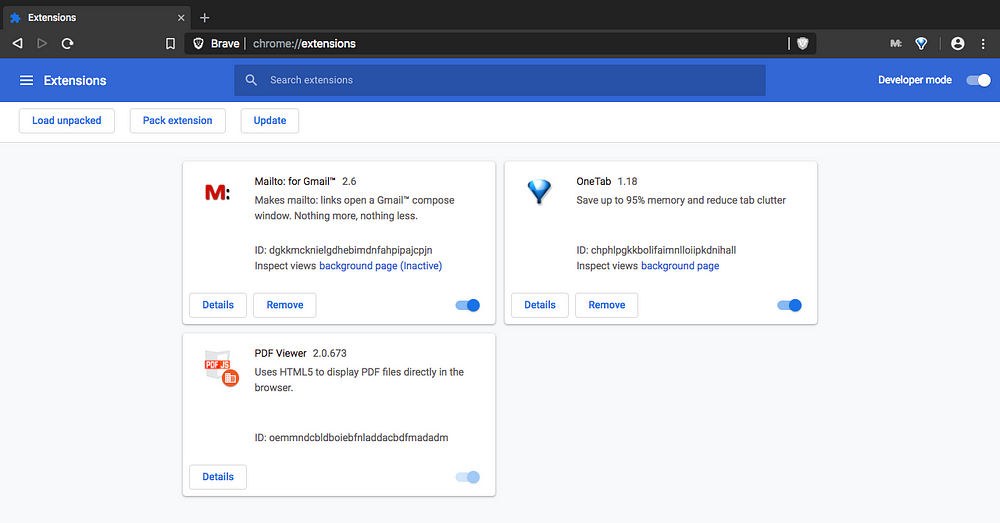
I am still using chrome for the dev tasks but have moved to brave for general browsing.
The big Picture
Basic Attention Token team is playing in the field of Attention economy and Digital advertising. They have realised the browser is a critical component for this and hence are concentration most of their resources on the browser. This seems like a very interesting approach to solve the Digital advertising. They are in it for the long run and they have got their priorities right. So for now I am bullish on BAT and brave. If you want to know more about BAT do read What is Basic Attention Token article
If you are already using Brave do let me know how has your experience been. Also what do you think of BAT? For official updates you can checkout Basic Attention Token
5 ways to breach-proof your Drupal Platform
With each passing day, the threat of security breaches to public facing digital platforms is only increasing. Nothing is safe, be it the corporate websites, a SaaS application or an e-commerce platform. However, much of the risk is minimized if the underlying platforms are fundamentally more secure. Drupal is one of the robust WCMS platforms that is built grounds up with Security and Performance in mind. It not only deploys the best industry practices when it comes to security, but it also has the most responsive community that rigorously and continuously performs security tests and rapidly provides patches and security measures to respond to vulnerabilities.
Valuebound has been among the Top 10 Global Contributors to the Drupal ecosystem and has a dedicated Drupal Security Center which continuously monitors the security aspect of Drupal and develops solutions to help the enterprise mitigate their security risks and build compliances around their business continuity process. While it is always advisable to have an expert who works round the clock to manage the Security of your Drupal installations, here are few handy suggestions to make any WCMS deployment more impregnable -
1. Upgrade, Upgrade, and Upgrade
From our experience and expertise in working with large and small Enterprise, we always recommend running the CMS on the latest version of the platform. Because most often, security breaches happen by exploiting vulnerabilities in codes that have not been patched. The Key reasons to upgrade your platform are -
- Upgrading avoids unnecessary expenses incurred owing to a security breach
- Using an outdated version of the platform exposes it to security vulnerabilities
- An update will fix technical issues & bugs
- New and enhanced features and functionalities can be added to the platform
Recently, Drupal has released its latest version - Drupal 8.6 - that includes a wide range of new features like Demo Data, Media Library, YouTube & Vimeo Embeds, Layouts, and Workspaces. In order to add new features and functionalities, we are working with several enterprises to upgrade or migrate their content management system. It should be noted that the older CMS versions are usually targeted as they are more vulnerable.
2. Strong User Management - A Must
Very often, a security breach is an inside job rather than an external hack. Keeping your website safe and sound, therefore, requires strong internal user management. Typically, in an organization, there are various stakeholders who require access to the website in order to manage different areas within it. The security habits of such users can be a potential risk for a security breach.
We recommend limiting account privileges on the need to have basis full access should be given very judiciously and only when it is absolutely required. We also suggest automated or prompt removal of accounts of users who have left the organization.
3. Know Your Hosting Provider
There are a bewildering number of choices when it comes to selecting a hosting provider. Of course, some were good, some were bad, some were good and then turn bad. Pantheon, Acquia Cloud, and Apache are some of the established players offering stable and enterprise-grade hosting services. For Drupal installations, it is always recommended to look for a hosting provider that offers security-first Drupal hosting solution with all the server side security measure like SSL.
4. Encrypt Sensitive Information
We recommend implementing proper certificates that help encrypt sensitive information. Proper deployment of SSL certificates helps protect your users, helps protect you and help you gain customers trust and sell more. Ask your in-house team or Drupal vendor to perform security audits at regular interval as this will allow you to fix the loopholes.
5. Take Backup regularly
Things can go wrong in multiple ways and there is a huge risk of losing all the data in case of security breaches or introduction of critical bugs while making changes or upgrading the platform. Hence it is important to take backup of your platform regularly. There are a host of service providers that offer backup and storage solutions to deal with such eventuality. There are other vendors who provide Backup, storage, and Recovery as managed services. The choice of vendor will depend upon the criticality of your application and the restore points demanded by your business.
Talk to our Drupal security expert to understand your Security Parameters and help you deploy the right Solutions, Tools, Systems, and Process that is just right for you,
Valuebound is deeply steeped in open source movement and specialize in Drupal CMS strategic consulting, development and dedicated managed support for media & publishing, e-commerce, and high-tech companies.
Implement These Modules to Make Your Drupal Site More Secure
A website with a security hole could be a nightmare for your business, leaving regular users untrusted. The security breach is not just about the website resources, but it could be putting up the website reputation at stake and injecting harmful data in the server & executing them. There could be many ways to do that. One of them is an automated script, which scans your website and looks up for the sensitive part and tries to bypass the web security with injected code.
I believe you might be thinking of your website now.
- Whether your website is fully secured or not?
- How to make sure everything ships on our website is generic? And how to protect them?
As a Drupal Developer, I’ve come across some of the contributed modules available on Drupal.org that can help your site in dealing with security issues. Still, I can’t assure, by applying those modules, you can safeguard your website. But it’s always recommended to follow the set guideline & utilize the modules to minimize the drupal security breaches.
Let’s take a look at those top and best Drupal modules:
Secure Pages
We all know that moving an application from HTTP to HTTPS gives an additional layer of security, which can be trusted by the end users. Unlike regular modules, you just don’t need to follow regular module installations instead your server should be SSL enabled.
Currently, it is available for Drupal 7 only.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/securepages
Security Kit
The Kit itself is a collection of multiple vulnerabilities such as Cross-site scripting, Cross-site Request Forgery, Clickjacking, SSL/TLS. With the help of security kit module, we can mitigate the common risk of vulnerabilities. Some of the vulnerabilities have already been taken care by Drupal core like clickjacking introduced in 7.50 version.
Currently, it’s available for both Drupal 7 and Drupal 8.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/seckit
Password Policy
This module is used to enforce users to follow certain rules while setting up the password. A web application with weaker security implementation, allow hackers to guess password easily. That’s the reason you get password policy instruction while setting up the password. It’s not just a fancy password, but secure & difficult to guess.
# Password should include 1 Capital letter
# Password should include 1 Numeric
# Password should include 1 Special Character
# Password should MIn & Max Character
This module is currently available for both Drupal 7 and Drupal 8.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/password_policy
Paranoia
This module looks for places in the user interface, where an end user can misuse the input area and block them. Few features that need to showcase here are:
# Disable permission "use PHP for block visibility".
# Disable creating “use the PHP” filter.
# Disable user #1 editing.
# Prevent risky permissions.
# Disable disabling this module.
Currently, it’s available for Drupal 7 and Drupal 8.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/paranoia
Flood Control
This module provides an Administrative UI to manage user based on UID & User-IP. There is configuration available to manage user restriction based on the nth number of the wrong hit by user ID/IP. We already know that Drupal core has a shield mechanism to protect their user with five unsuccessful logins hit, users get blocked for an hour/minute. With the help of the contributed module, we can dig it a bit.
Currently, it’s available for Drupal 7.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/flood_control
Automated logout
In terms of user safety, the site administrator can force log out users, if there is no activity from the user end. On top of that, it provides various other configurations like:
# Set timeout based on roles.
# Allow users to log in for a longer period of time.
# User has the ability to set their own time.
Currently, it’s available for Drupal 7 and Drupal 8.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/autologout
Security Review
This module checks for basic mistakes that we do while setting up a Drupal website. Just untar the module & enable it. This will run an automated security check and produce a result. Remember this won’t fix the errors. You need to manually fix them. Let's take a look at some of the security features that need to be tested by the module:
# PHP or Javascript in content
# Avoid information disclosure
# File system permissions/Secure private files/Only safe upload extensions
# Database errors
# Brute-force attack/protecting against XSS
# Protecting against access misconfiguration/phishing attempts.
Currently, it’s available for Drupal 7.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/security_review
Hacked
This tool helps developer avoid adding messy code directly to their contributed module, instead of applying patches or new release update. It works on a very simple logic. It scans all the modules & themes available on your site. Download them and compare it with an existing module to make sure modules/themes are on correct shape. The result will give you information on changed module/theme and the rest of the thing you are well aware of - what needs to be done?
Currently, it’s available for Drupal 7 and Drupal 8.
Ref URL: https://www.Drupal.org/project/hacked
All of the above modules are my recommendation that a Drupal website should have. Some contributed module will resolve your security issues by providing correct configuration and some of them are just an informer. They will let you know the issue. But you need to manually fix those issue.
Further, these contributed modules provide the atomic security based on the complexity of your site and types of user available. You can look up for the security module and protect your site against anonymous.
We, at Valuebound - a Drupal CMS development company, help enterprises with Drupal migration, Drupal support, third-party integration, performance tuning, managed services, and others. Get in touch with our Drupal experts to find out how you can enhance user experience and increase engagement on your site.
Content Management System: The Past, Present and The Future
Over the decades, the Content Management System has seen an unprecedented growth from static web pages built on HTML to customized sites developed using PHP to give personalized experience. Initially, in the 1990’s, we had flat HTML files. Then there was Dynamic HTML to create interactive and animated websites by using a combination of a static markup language.
Here is the look of Apple.com at the very birth of the World-Wide Web in 1992.

Picture by - The Telegraph
Then there was GeoCities, a web hosting service, later acquired by Yahoo in 1999. During this time, GeoCities was the third-most-visited site on the World Wide Web. It was the first kind of web-based CMS that allows users to manage their website. This is a concise history of CMS in the 1990s. On contrary to this, 2000’s seen the massive development in this niche from basic HTML & DHTML web pages to proprietary and open source CMSs.
Web-based CMSs in 2000’s
In the first part of the 2000’s, Open source CMSs like Drupal, WordPress, and Joomla were launched. These solutions were primarily focussed on one thing - making the CMS easier and more powerful for non-technical people
Initially, these CMSs followed a similar pattern. They contained both backend and the front-end of the website and store all your assets, images, texts, files and others to store, manage, display and download.
Then came RSS feed which has to shoehorned onto a standard website. This was followed by mobile devices then came responsive designs. Earlier, web pages for mobile were separately built for not so smartphones like Blackberries. These were on the frontend.
Backend had texts, multimedia assets, files, images. This was followed by the requirement of comments on the post - a user-generated content that can be stored and people could leave comments by creating accounts or anonymously. These were stored in backends.
As people/companies started using CMSs particularly the above-mentioned open sources, the demand for more functionality was raised like giving accounts to people who are managing content, editors, writers, and administrators.

This led to building account functionality and the users had accounts where they can come and register on the site as it will help marketers to track their information. This required a login system so that user can create a profile which has to have user permission system as not everyone can have admin access. Later, this permission system was built into a CMS.
Since administrators of the site didn’t know HTML, CSS or javascript, they wanted layouts so that they can create their own designs. As a result, developers had to come up with drag and drop feature to create a layout, which was followed by other developments like the integration of 3rd party applications such as shopping cart, analytics, CRM and ERP.
Fast-forward to today
The CMS of today puts the content first. The CMss are built in such a way that it should be robust, scalable, secure and more importantly, cater to unique business needs and provide a seamless experience to stakeholders. Let’s discuss some of the most essential features and functionalities of modern-day CMS where personalization, responsiveness, and integration are plays a pivotal role.
Centralized CMS
The Centralized CMS allows users to collect, manage and distribute the digital content from a single location. Typically, it supports multiple users in a collaborative environment wherein a user from a different community can contribute content. Most CMSs include Web-based publishing, format management, history editing, and version control, indexing, search, and retrieval.
Context-Aware Content Management
Today, organizations are increasingly asked to deliver more value from their online marketing efforts and marketer to do more with less. In this scenario, contextually aware content delivery comes into play as it helps to deliver more value for less effort. CMS Wire defines Context-Aware Content Management as
“Systems that understand how, what and when to deliver content given an astounding number of parameters. Interfaces will be separate, and unique to the devices, the situations and the platforms that consumers choose.”
Multichannel & Omnichannel Publishing
Simply stated, multi-channel publishing means delivering a publication to readers in many ways at the same time while omnichannel publishing aims to provide a seamless and consistent experience to customers across various platforms such as website and mobile device etc.
Headless & Decoupled CMS
Readers are often confused between Headless CMS and Decoupled CMS. Headless CMS is a subset of decoupled CMS and has no default front-end system to determine how the content is presented to the end user. Read on our previous post where we have discussed how headless Drupal is driving user experience.
Whereas decoupled CMS segregates the back-end from the predetermined content publishing front-end delivery channel and places an API between them. This model provides web developers a great flexibility to innovate and help business owners future-proof their project. Further, it allows organizations to refresh the website design without re-implementing the whole CMS. With all these advantages, the decoupled CMS has gained a major traction in both the Drupal as well as WordPress communities.
Integration For All
Today, there is hardly any web development project that doesn’t involve the integration of 3rd party applications. These applications are used for varied purposes and must have consumer features to make sure you have proper site analytics and marketing metrics for your growing business. Have a look at our previous post where we have discussed various 3rd party integration options available within the Drupal ecosystem.
Future-proof your CMS
With the digitization at its peak, no software lasts forever and has to be upgraded at a regular interval to fulfill growing market demands. For instance, you can see different versions of Drupal, the latest is Drupal 8.6.0 and the upcoming is Drupal 9. Future-proofing a CMS means you need to be prepared for the growing market demand and should be able to figure out what ideas should pursue and which should you avoid.
User Experience
Typically a CMS has different stakeholders such as business owners, content developers, marketers, developers, and customers. The different stakeholders, who have different roles to play, require a seamless experience to achieve their goal. This requires a project for experience and not for devices. There are several things which need to be figured out before building a project.
Here user experience is the core of any project and requires things to be done in order. The development of any project starts with a user persona as they define expectations, concerns, and motivations, helping design teams to understand how to design a product that will satisfy users needs.
Chatbot
Also referred as conversation interface, this has turned out to be a must-have feature for all sorts of business whether it is media & publishing, hi-tech or e-commerce. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global chatbot market is estimated to reach USD 1.25 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 24.3%. Further, the report revealed that the development of chatbot will substantially minimize operation costs.
Innovation in artificial intelligence and machine learning - the key component of chatbot will boost its features. There are numerous advantages to deploying chatbots as part of your digital strategy, such as:
- Conversation interfaces can be operational 24*7*365 days a year.
- It can process a chunk of requests simultaneously.
- Using chatbot, organizations can get real-time insight into their customer's preference.
- These are cost-efficient as it easily gets configure to meet different requirements. Updating cost is relatively low.
- It can easily record data, trends, and metrics to monitor interactions and adjust their processes and responses accordingly.
- These are time-saving as it helps companies save time by answering the queries raised by clients.
Virtual and Augmented Reality
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are the next two big disruptive technologies, companies are focussing on. The rise of AR means that publishers will now be able to bring stories to life in a whole new way. Read on why virtual reality is the next big thing in the media industry and how it can help increase revenue?
Although the decades-long story can’t be narrated on one single post, I have tried to summarise the past, present, and future of the CMS as much as possible. The gist of the entire post is that technology keeps on evolving so does our and users necessity. In the fast developing digital era, it’s crucially important for media and publishing companies or any other to keep up with the latest technology in order to stay ahead of our competitors and provide an enhanced experience to users, seamless navigation and interactive interface as required.
We, at Valuebound - a Drupal web development company, help enterprises with Drupal migration, Drupal support, third-party integration, performance tuning, managed services and others. Get in touch with our Drupal experts to find out how we can help you with building a CMS that offers an enhanced user experience and boost engagement.
Reference
Make Your Drupal 8 Website Accessible To All
Have you ever thought about how people with visual & auditory impairment or cognitive or physical disabilities access websites? People with disabilities can access the web as we do only when a website and/or mobile apps have been developed keeping a different set of audience in mind. This is where web accessibility comes into play.
Making a site accessible isn’t that difficult to implement as it seems to be. You just need to understand the underlying issues that make a site difficult or impossible to use by the challenged people.
So what is web accessibility?
Web accessibility is all about making sure that websites work for the widest possible audience.
According to the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) - an international community - web accessibility means that websites, tools, and technologies are designed and developed so that people with disabilities can use them.
Importance and benefits of accessibility
Expands your audience base
An easily accessible web provides equal access and equal opportunity to people with disabilities thus resulting in an increased audience (more users) and increased effectiveness (more useful).
Good for SEO
Accessibility has a direct correlation to developing best practices for SEO. It increases the visibility of the web page.
Grow your Business
The most obvious benefit of building accessible websites is to help businesses and organizations widen their reach.
Build Positive Public Relations
Building an accessible website also builds your reputation. Why not stand out from your competition by being accessible to everyone and demonstrating social responsibility?
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.0
Level A
The most basic web accessibility features are:
- provides text alternatives for non-text content
- Provides an alternative to video-only and audio-only content
- Accessible by keyboard only
Level AA
Deals with the biggest and most common barriers for disabled users:
- Text can be resized to 200% without loss of content or function
- Do not use text over image
- Suggest fixes when users make errors
Level AAA
Deals with the most complex level of web accessibility
- Provide detailed help and instructions
- Do not use text over image
To get a full list, refer WCAG 2.0 checklists
Ways to make your website accessible
The heading is an outline of your webpage. Use headlines to introduce content, they are labels, not a statement.
Heading 1 is the most important for the page use it as the title of the page. Heading 2 is subheadings of the H1. Use it to divide content into scannable blocks. H3 is for subheadings of the H2.
Below are the guidelines for the heading:
Nested Heading
The heading is an outline of your webpage. Use headlines to introduce content, they are labels, not a statement.
Heading 1 is the most important for the page use it as the title of the page. Heading 2 is subheadings of the H1. Use it to divide content into scannable blocks. H3 is for subheadings of the H2.
Below are the guidelines for the heading:
- Every page should have an h1 heading
- Headings must be properly nested
- Headings are used for structure, not formatting
- Don’t hide headings

Form Accessibility
- Every Form elements must have a label and announced before the input
- Keyboard Accessible Field
- Use Inline Form error
- Always include a button for users to submit their form information

Add an Alt Text to All Images
Alt text is a replacement text of the image if it fails to load. ALT text is accessed by screen reader users to provide them with a text equivalent of images. It also helps in improving SEO.
Screen Reader Output With ALT Tag

Screen Reader Output Without ALT Tag

Aural Alerts
Users with visual impairment cannot see all visual updates of the page such as color changes, animations or texts appended to the content. In this case, Drupal provides a JavaScript method Drupal.announce() which creates an “aria-live” element on the page. Drupal.announce accepts a string to be read by an audio UA. Below is the example of aural alert.
Drupal.announce(
Drupal.t('You look beautiful today.')
);
Text over images
Text over an image shouldn't be completely avoided, if required then make sure that the text is both legible and readable to users. To handle this, maximize the contrast on your pages among graphics, fonts, and backgrounds.
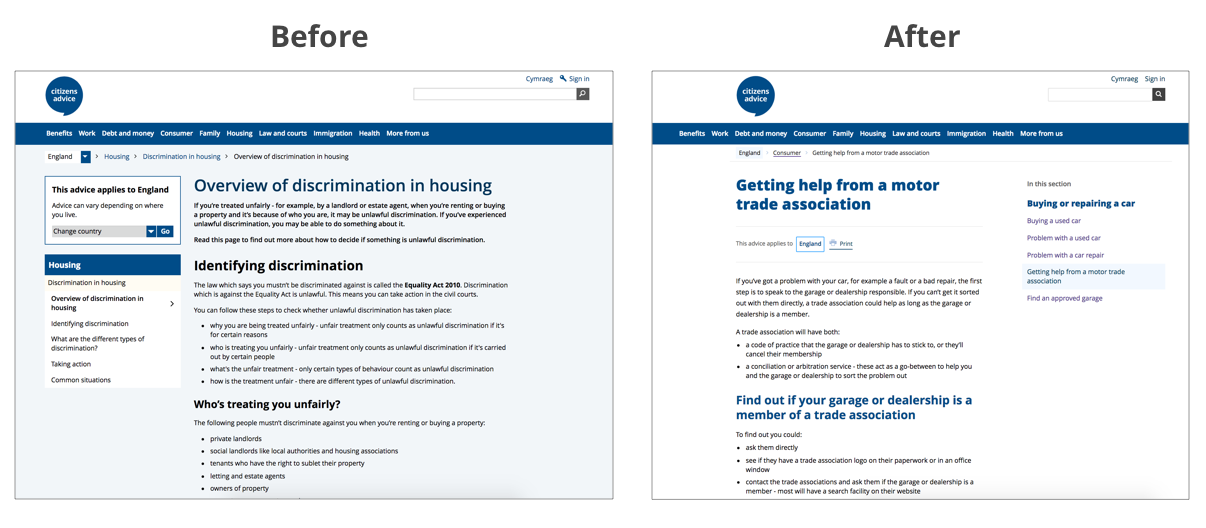
The removal of the blue background from the image is giving maximum contrast. The content is more clear and accessible to read.
CSS Display Options
None of your content hides completely by using the hidden attribute or setting display. Users can't see it and screen readers or search engines can't read it. To help with this, Drupal 8 has adopted three new display classes: (1) hidden, (2) visually-hidden (3) invisible.
Hidden: Hides an element visually and from screen readers
Visually-hidden: Hides an element visually but exposed to screen reader users
Invisible: Hides element visually and from screen readers. Also, it doesn’t affect the layout
Constrain tabbing
Drupal 8 introduced JavaScript feature, called tabbing manager, to guide a non-visual user to tabbing contextual links when the global edit mode is enabled. Use below code to invoke the tabbing manager.
var tabbingContext = Drupal.tabbingManager.constrain($('.contextual-toolbar-tab, .contextual'));
A set of elements is passed to the constrain method. Pressing the tabbing key will only move between the tab-able elements in this set of elements.
To remove the tabbing constrain, the release method must be called on the tabbing context object.
tabbingContext.release();
Drupal 8 Contributed Modules For Web Accessibility
Automatic Alt text
When a user doesn’t provide Alt text for images, Drupal 8 uses Microsoft Azure Cognitive services API to generate one.
Text Resize
This module generates block to quickly change the font size of text on your Drupal site.
CKEditor Accessibility Checker
This module provides the Accessibility Checker plugin in your WYSIWYG editor to inspect the accessibility level of content created in CKEditor and immediately solve any accessibility issues found.
Block ARIA Landmark Roles
This module adds additional elements to the block configuration forms that allow users to assign ARIA landmark role and/or ARIA labels to a block.
To sum up, web accessibility is all about making your site available to as many users as possible. There shouldn’t be any hindrance for disabled people in the digital world. This post focuses primarily on discussing the ways you can make your site accessible using Drupal 8 contribute modules.
We, at Valuebound - a Drupal web development company, help enterprises with Drupal migration, Drupal support, third-party integration, performance tuning, managed services and others. Get in touch with our Drupal experts to find out the ways you can use big data for your business.
Below given is a presentation on "web accessibility in Drupal 8"
10 Great Examples of Drupal Commerce Websites
Selling products online is not just about successful eCommerce, but managing data as well as customer engagement across the platform. Drupal integrated with Drupal commerce offers unprecedented results that are highly secure, stable, create engaging web experiences and drive website traffic. The combination also ensures that both users and customers have a seamless experience, reduced development time, easy maintenance, and control of SEO, CRO, and website analytics tool among others.
In this post, we have shared 10 great examples of websites (from different industries) built on Drupal commerce that are setting the benchmark. These will surely help you with the creative process. Read on the features, functionalities and 3rd party integration used by these companies.
1. URBANY'S
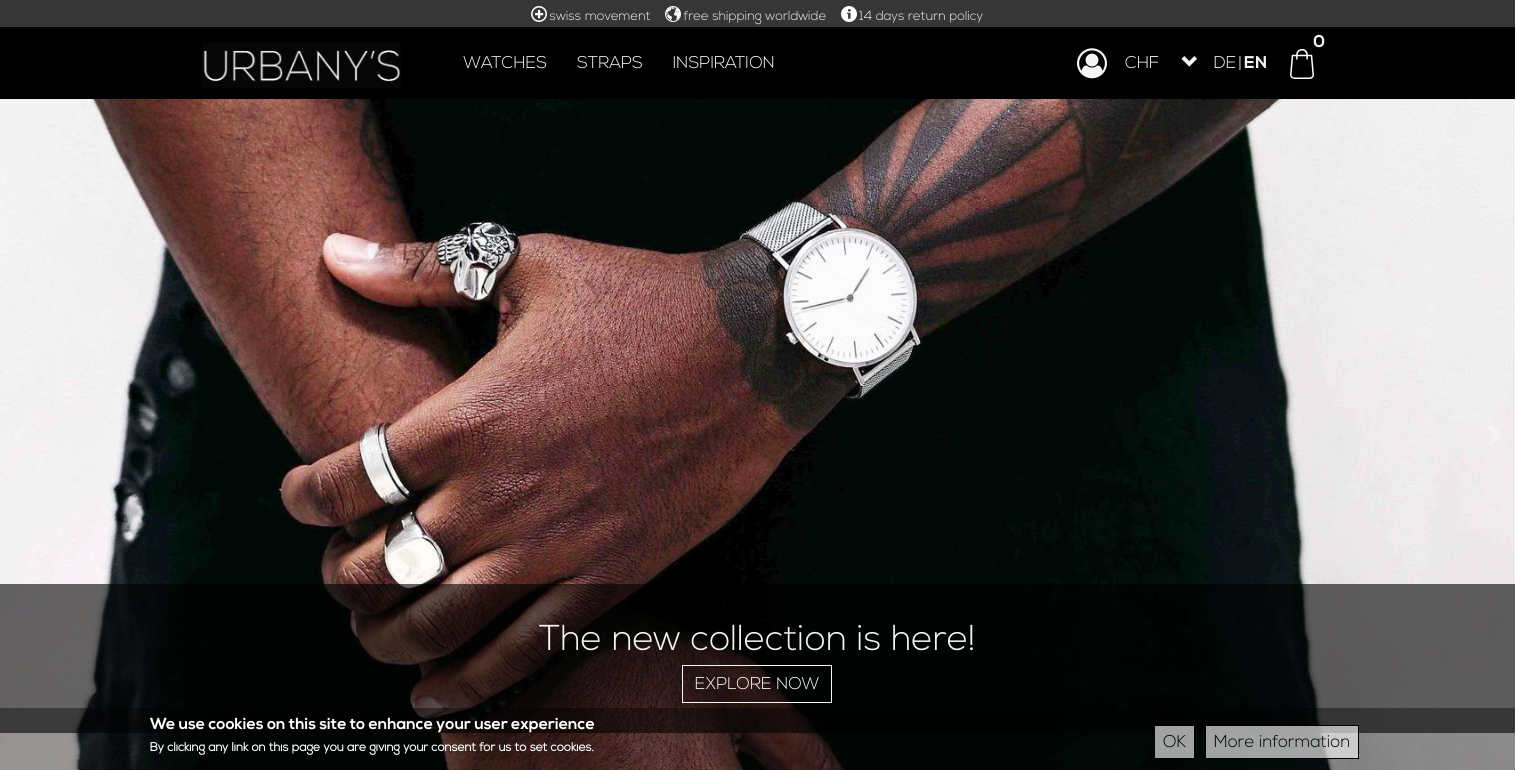
When your website is all about fashion accessories, you need a site that draws people attention, offers seamless navigation and secured payment gateway. The Swiss e-commerce store leverages Drupal commerce as it was specifically designed to fit in with Drupal 7 using the latest features and APIs. However, the store leverage Drupal 8 for its improved loading speed, mobile toolbar and responsive theming.
Further, Bootstrap is used as a front-end framework due to its responsiveness, development speed, customization, simple integration and other. The site is integrated with analytics tools like Google Analytics and Matamo for measuring the success and utilizes the payment processing service of Visa, Mastercard, Paypal, American Express.
2. Lush
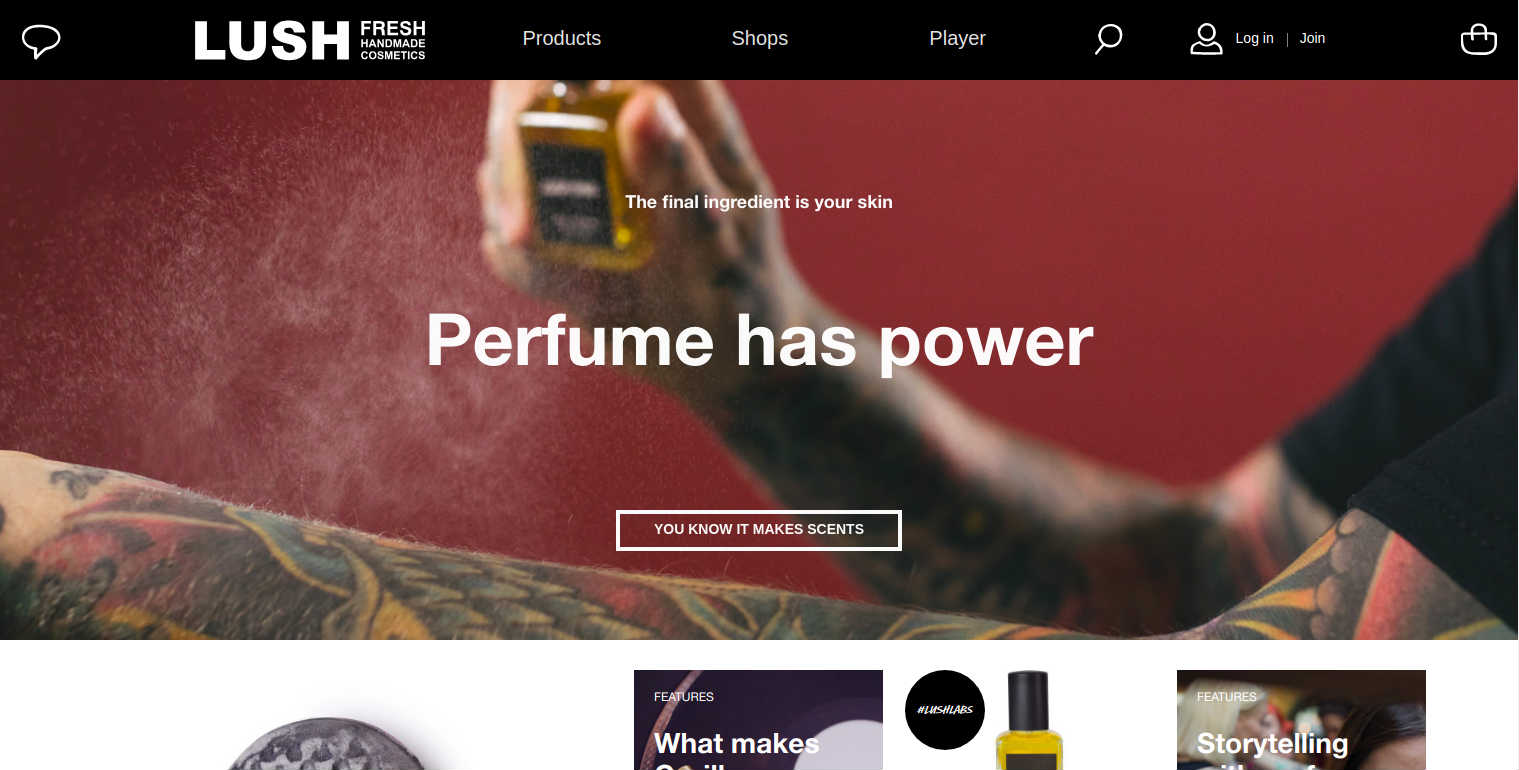
British skincare and handmade cosmetics store Lush presents a clean astonishing website that features attractive colors and fonts. Built on Drupal 7, the website is complemented by a wide range of features such as a single page checkout to pay securely with Mastercard, PayPal, Visa, American Express and BitPay. Lush uses CloudFlare as a content delivery network as it automatically optimizes the delivery of web pages to reduce page load time.
The e-commerce store is integrated with Mautic to connect all of their digital properties and channels. Further, the site uses Varnish as a caching tool and Google Analytics as a digital analytics software to measure its success.
3. Olsson & Gerthel
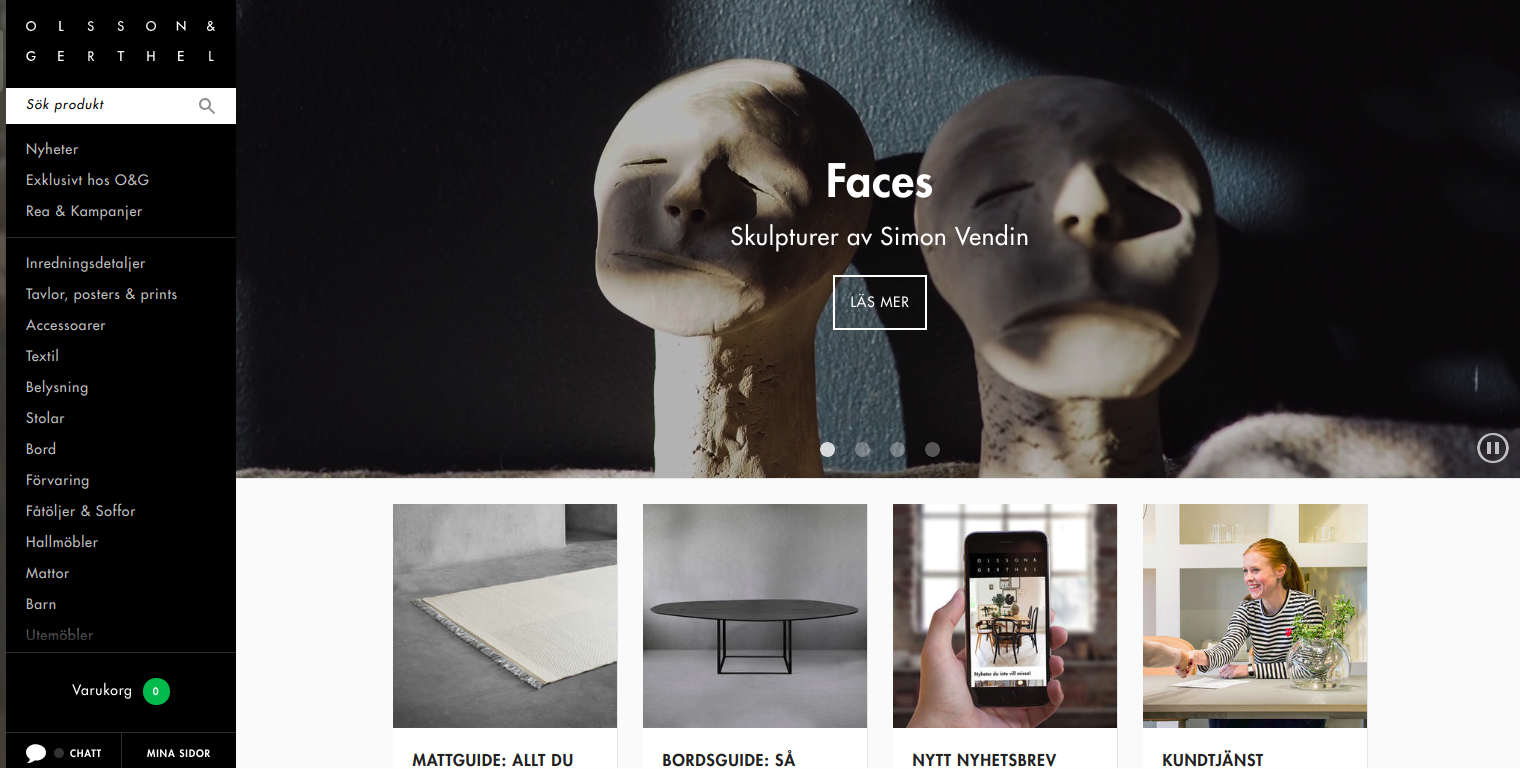
Olsson & Gerthel - a Sweden-based furniture store is well-known for features world-class designers on their Drupal Commerce website. The site stands due to its up-to-date style, seamless navigation and more importantly, a side panel makes it easier to filter the object as per our requirement. The e-commerce store uses Zendesk Chat for the live chatting feature, Google analytics, and CKEditor - a WYSIWYG text editor that allows the user to write content directly on web pages or online applications.
4. Pam Kerr Designs
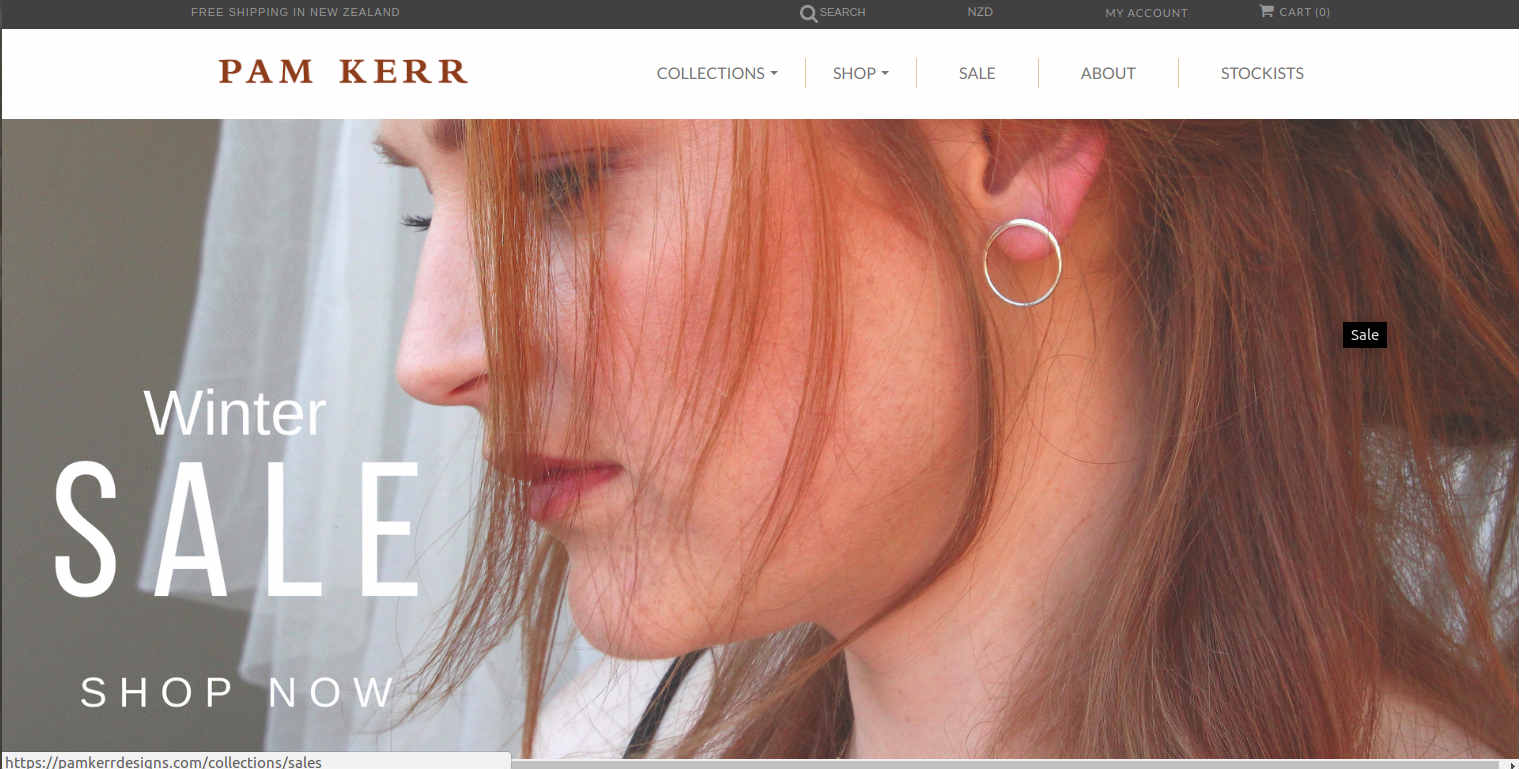
New Zealand-based online jewelry store Pam Kerr designs uses Drupal commerce for their website to showcase the latest collections. A simple layout and clean design give an enchanting and smooth user experience. The e-commerce site is integrated with Stripe for payment processing. Built on Drupal 7, the site offers various payment options including PayPal, Visa, Mastercard, and American Express. Google PageSpeed has been utilized as a caching tool and Google Analytics for measuring the success.
5. Fooda
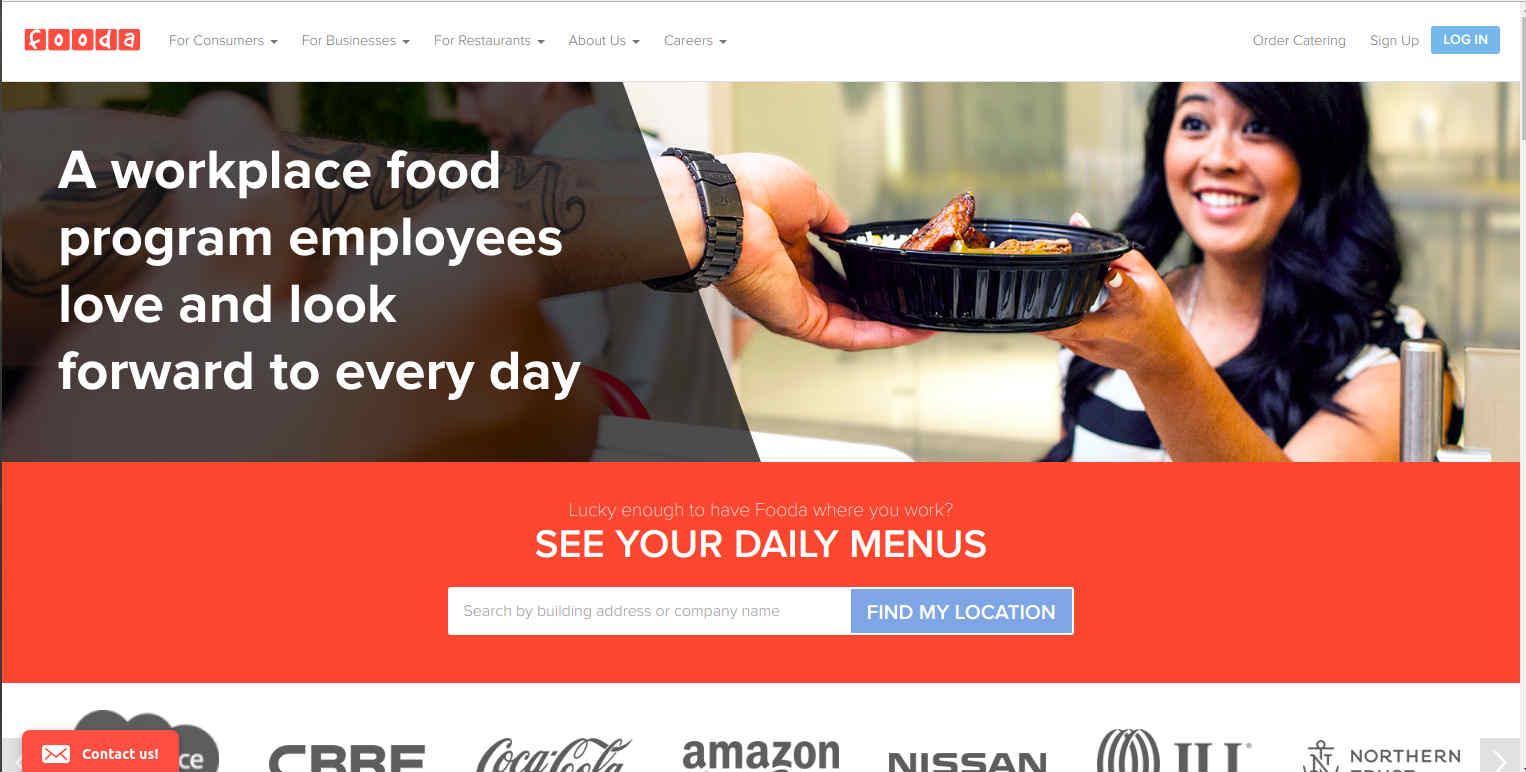
Fooda, an American meal services firm, partners with companies and office building to provide a restaurant-based meal. The website, which uses Drupal Commerce for a clean layout and easy navigation, uses Bootstrap as a front-end framework. Third-party APIs are also utilized throughout the site, including HubSpot marketing automation tool and analytics tool like Crazy Egg, Optimizely, Google Analytics, Matomo, Mixpanel. Further, AdRoll - an advertising network - is used to collect, analyze, and act on their customer data to deliver marketing campaigns.
6. Eurocentres
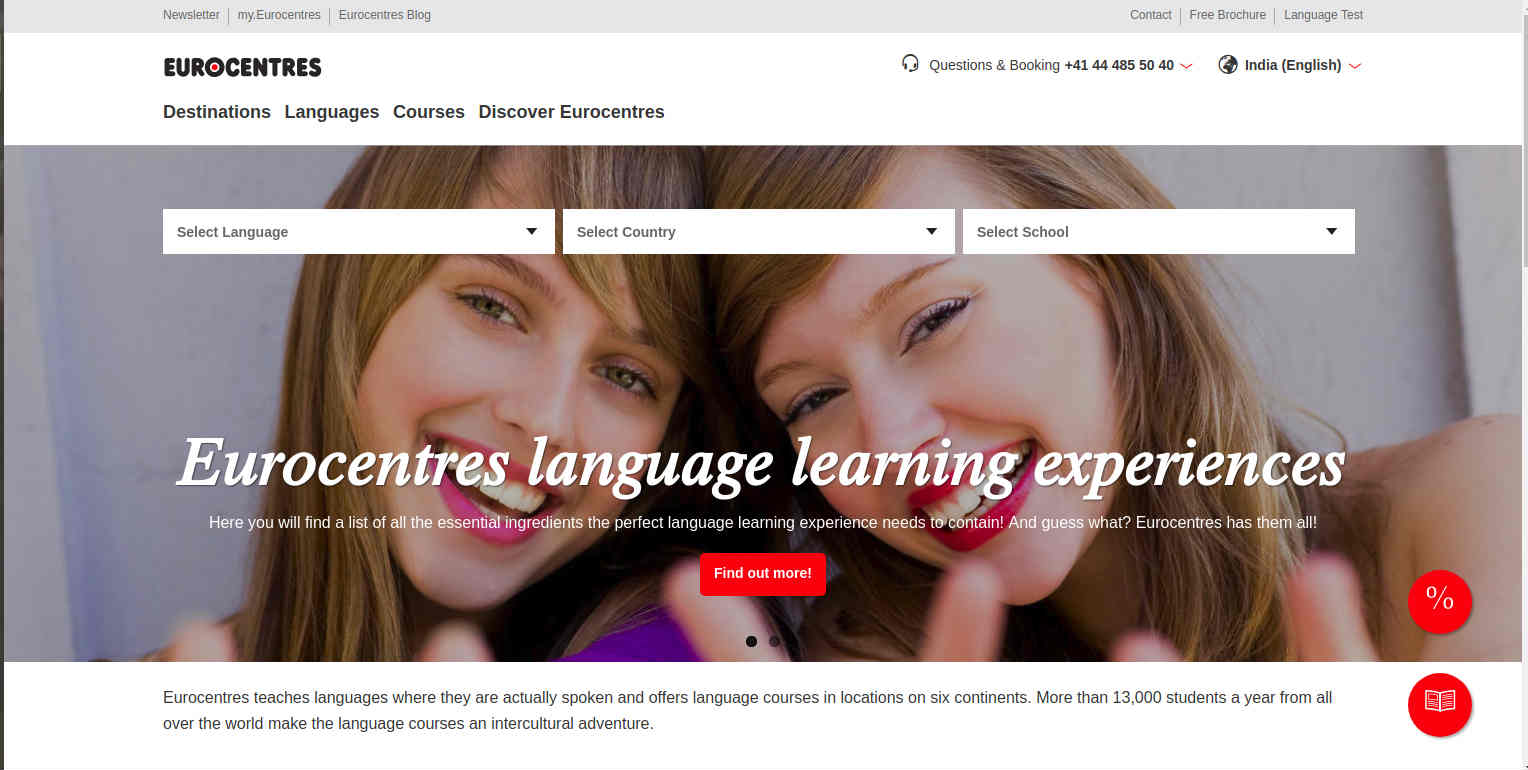
Switzerland-based Eurocentres is one of the leading organization that offers academic and professional English language courses for adults and juniors on six continents. Nearly, 13,000 students enroll every year from all over the world. Built using Drupal commerce, Eurocentres offer a rich experience, seamless navigation to search destinations, languages, and courses offered. The language learning site uses Visual Website Optimizer and New Relic for analytics and Varnish as a caching tool.
7. QDOS
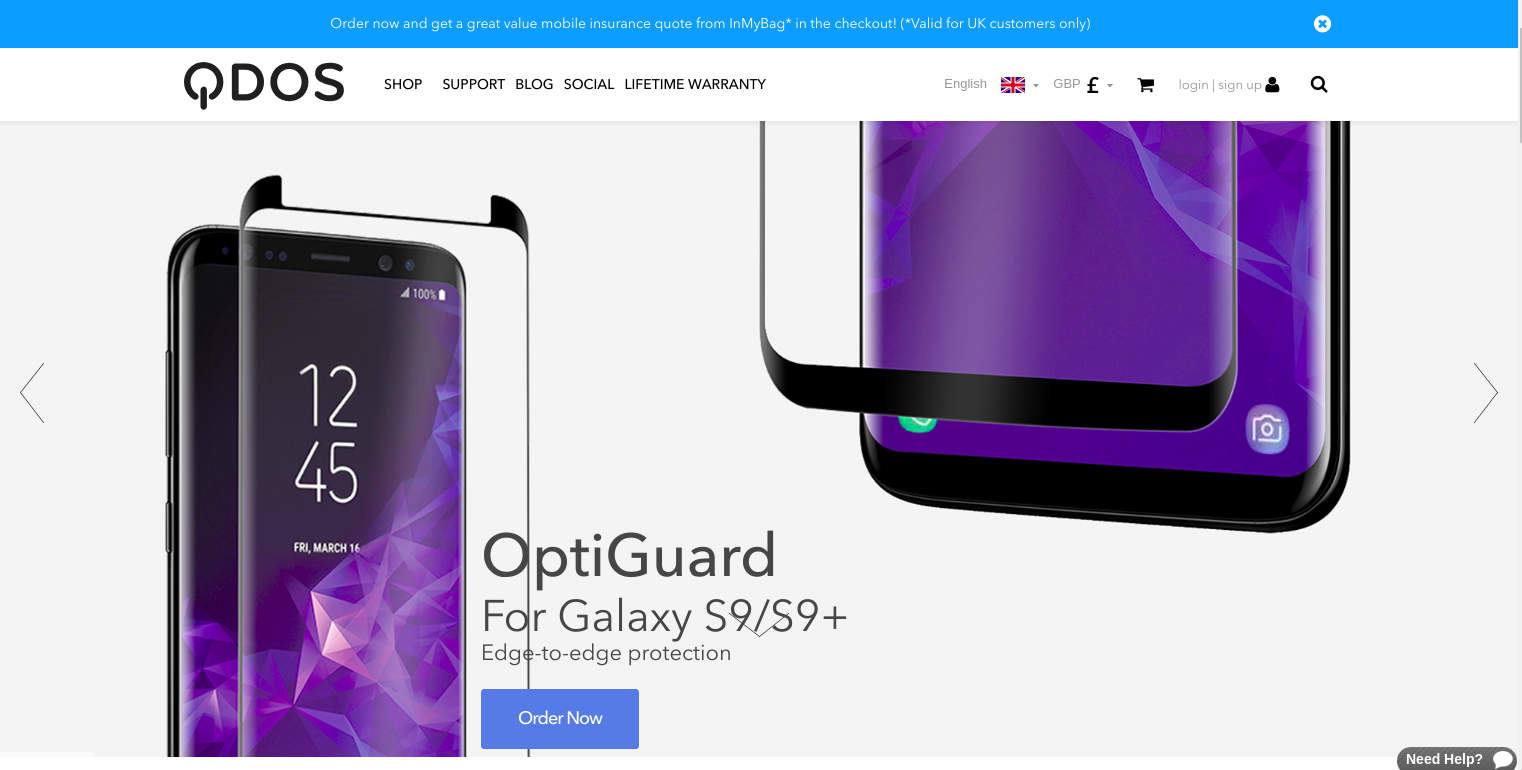
The UK-based QDOS - an e-commerce store for phone screen protectors, cases & power products - is beautifully designed to offer seamless navigation and find a relevant product on the homepage itself. The online store, which is built on Drupal commerce, boasts different functionalities like multilingualism, 3rd party integration of various social media channels and accept payment in different currencies like EUR, GBP, and USD. QDOS also offers a great alternative to signing up with your Facebook account, in lieu of creating a new account.
Third-party APIs are also utilized throughout the site, including MailChimp for marketing automation, LivePerson for live chat and Gauges & Google Analytics for measuring success.
8. Tuan Nguyen Photography
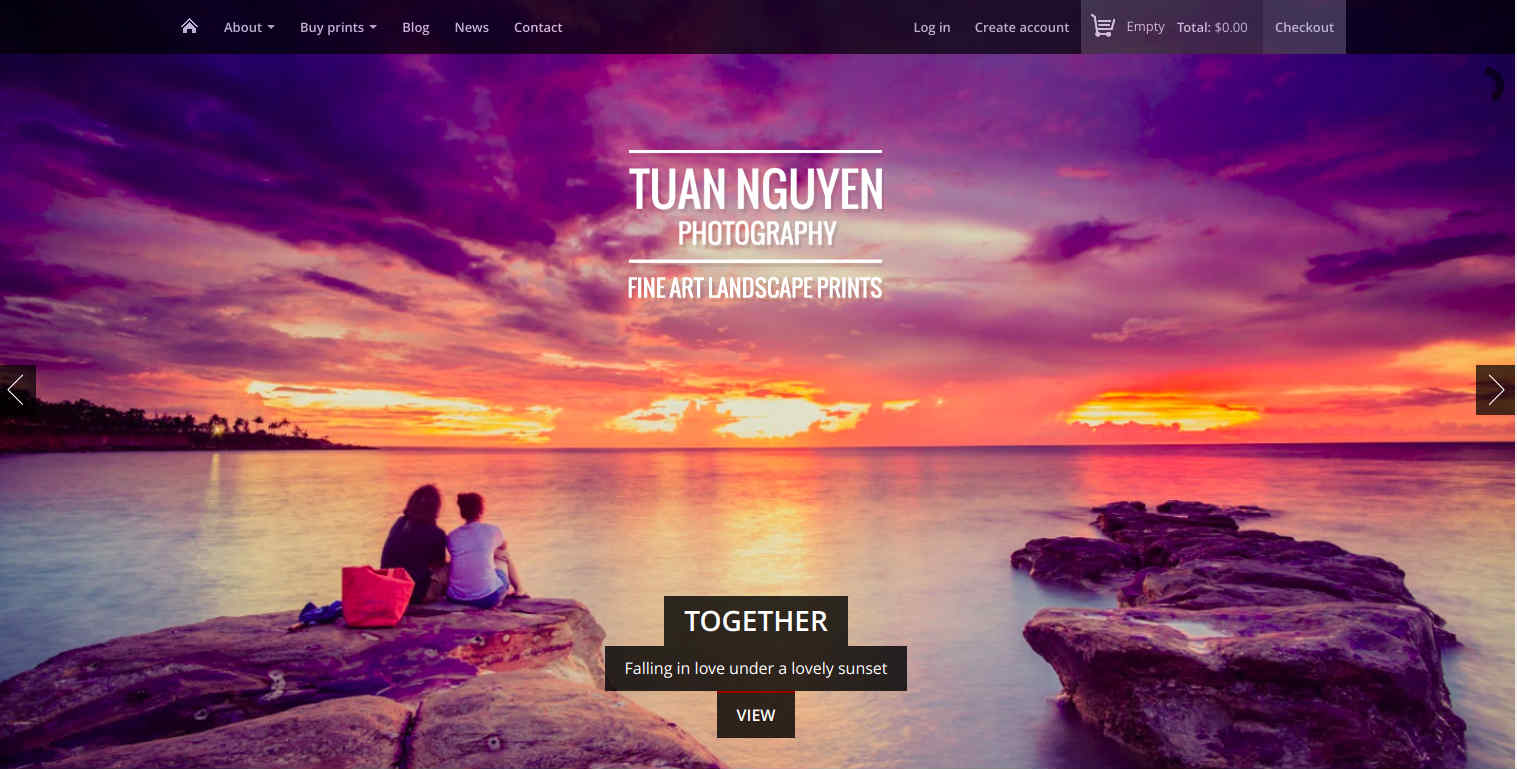
Landscape photographer Tuan Nguyen uses Drupal commerce to develop to share high-resolution landscape photographs. The online store boasts an image carousel on the homepages segregated into different columns. Though the site looks very simple and elegant, it has fast page downloading, seamless navigation and integration with social media channels to promote the content and drive users back to the site.
9. Muzeo
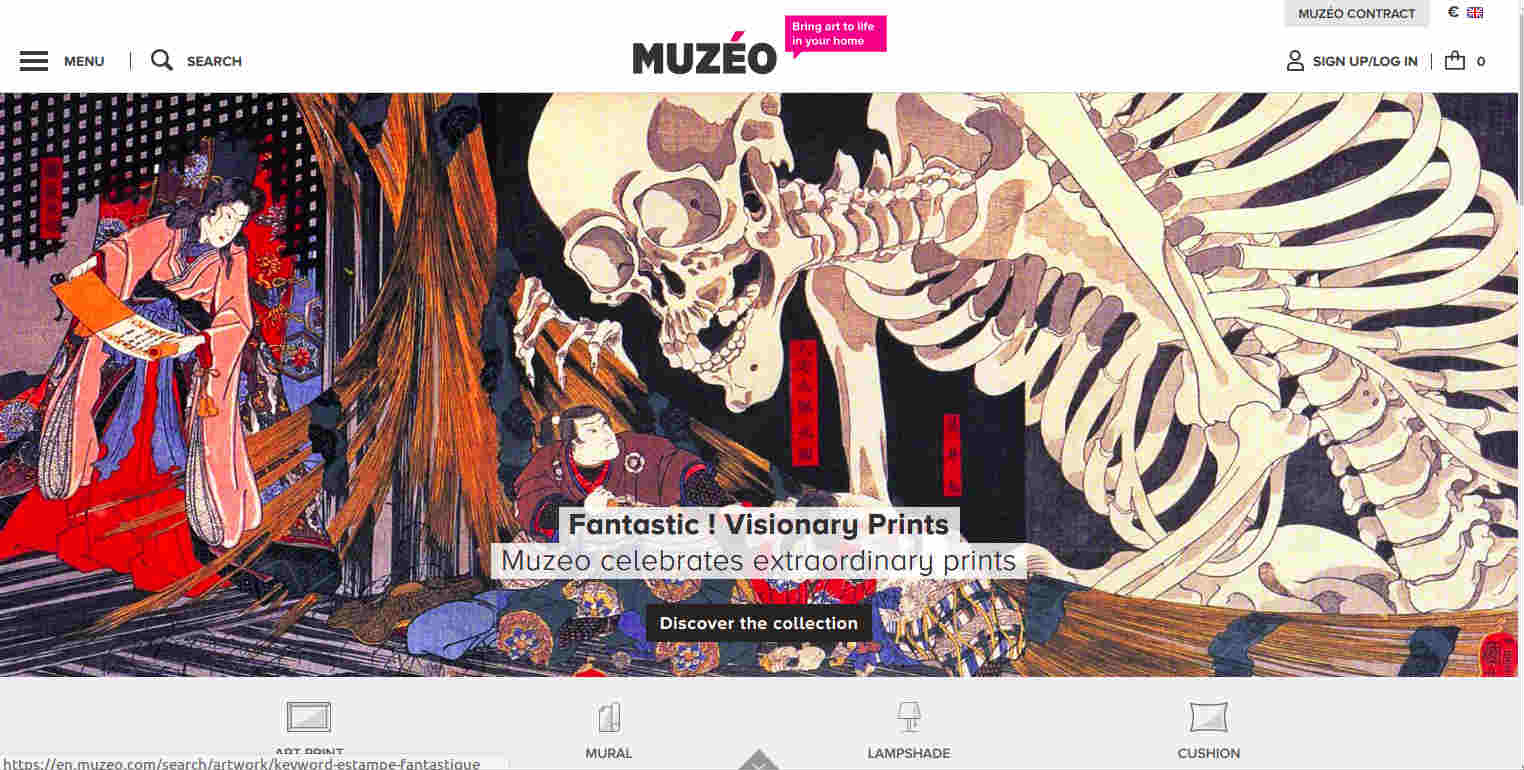
French art gallery Muzeo offers a state-of-the-art experience with high-resolution pictures showcasing different categories that redirect to a specific landing page where you can filter the art pieces accordingly and purchase. Built on Drupal commerce, the homepage features a menu section on the top left side to redirect to different landing pages. The art store also allows users to narrow their search by filtering the pieces using header and side panel. Whereas the footer section features payment options, return policy, rating, comments, and third-party integration with social media channels. Users can also subscribe to the newsletter by just entering their email IDs.
10. Guerlain
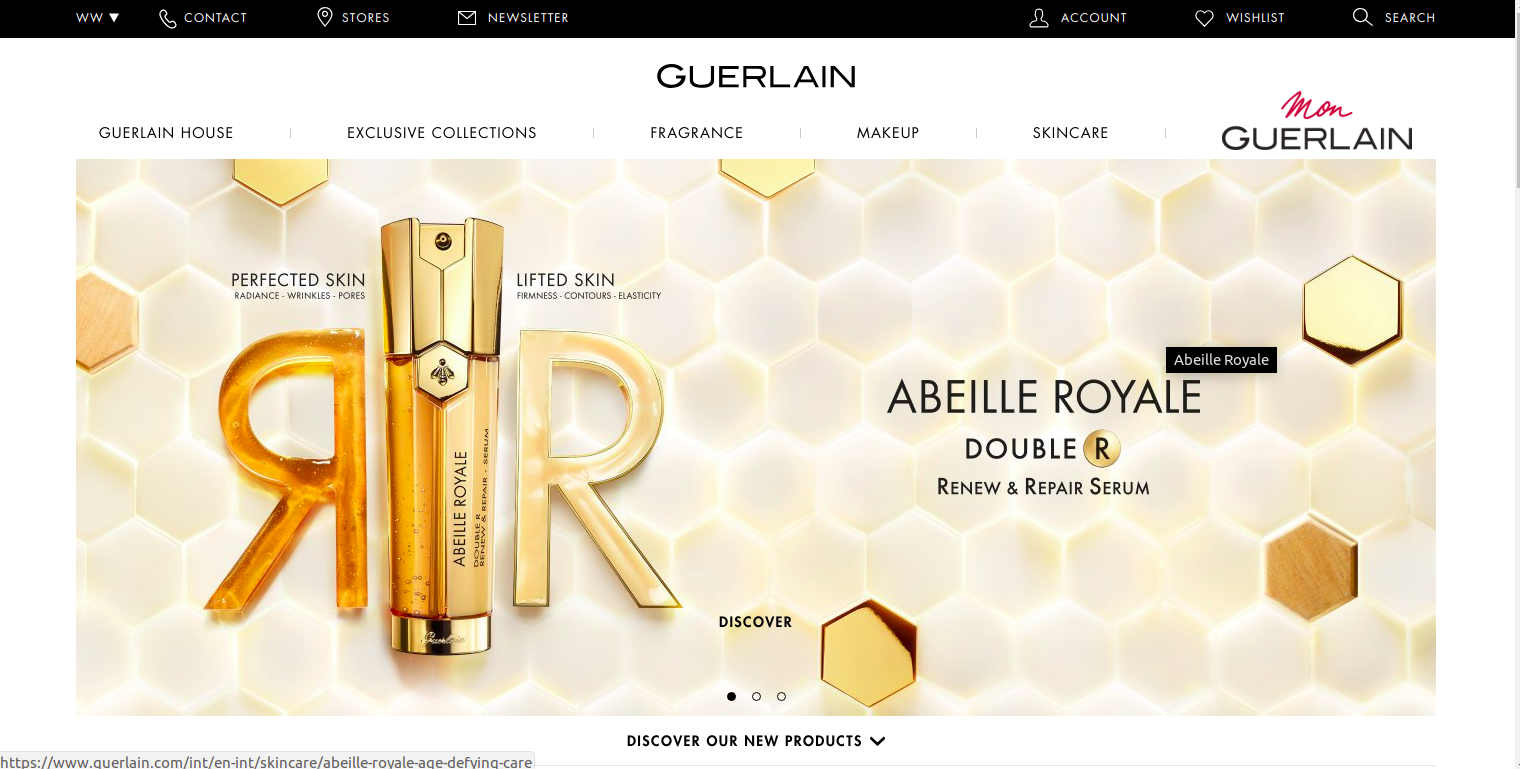
Founded in 1828, French perfume, cosmetics, and skincare house use Drupal commerce to feature its products online. The header houses different categories where you can find a list of products along with the new product available in that category. Each product has a dedicated landing page with product description, an option to add on the wishlist and zoom the product images to have detailed look. Landing pages also include point of sales option where you can find your nearest store and share button to share the products with your kith and kin.
We, at Valuebound - a Drupal web development company based out of New York, help enterprises with Drupal migration, Drupal support, third-party integration, performance tuning, managed services, and others. Get in touch with our Drupal experts to find out how you can enhance user experience and increase engagement on your site.
Suggested Readings:
Medical Device CMS - The What and Whys
In the traditional pharmaceutical business model, it seems like all the efforts were put into addressing the physicians needs to boost sales. However, the scenario has changed drastically in the past few years and the focus is more inclined towards customers alongside physicians and payers.
Current business model driven by advanced technology is giving patients an opportunity to have a say and become more and more involved in their healthcare issues. This is especially true when it comes to millennials, who are not very satisfied with the information provided by their healthcare experts. Hence, people are leveraging the power of wearables to measure and track their fitness and vital signs like blood pressure and heart rate.
On these premises, it’s not difficult to agree with the growing importance of online presence and building credibility to boost sale. Having said that CMS provides medical practitioners space to share the know-how of new and upcoming medical devices. As a result, information sharing is becoming a critical part of the marketing strategy. So let’s dive straight into the basics of CMS, what does it manage and why does it matter for your industry.
What is CMS?
A CMS is a software application that is used to create and manage digital content. Using this, medical device makers can handle a vast amount of product information that is required to bring to market. It can be also used to present medical device information to a diverse set of stakeholders as a means of increasing quality management and regulatory compliance while reducing risk.
While selecting a CMS for pharmaceutical products, you need to look at different aspects such as ease and speed of setting up a user friendly website, performance optimization, security, what can be done if there are unexpected changes, volume variations, demands for major workflow changes, and other problems specific to the medical device industry.
Regulatory compliance, website performance, personalization, and SEO are the other key components you need to look at. Here are the 5 reasons why a business needs to invest in a web CMS:
- Facilitates frequent content updates on the web properties
- Aids in effective content management & collaboration
- Ensures device & platform compatibility for the web properties
- Effortless customization options at your fingertips
- Web experience management
What does CMS manage?
In the medical device industry, consistency is the key to brand awareness. Undoubtedly, due to the rising competition and concerns, the approval of new drugs and medical devices has been marginally declined by the US FDA. To overcome these factors, pharmaceutical companies are investing in their brands. After all, increasing brand awareness is an important strategy to boost a company’s competitiveness.
An easy to use medical device CMS lets your content developers and marketers engage with a prospect, maintain the consistency throughout different collaterals such as blogs, news, product pages, corporate content, industry analysis, announcements, testimonial, and others.
In the medical devices industry, such components could be company information, product information, training materials, investors information, news, press release et cetera.
Here making an informed open source CMS choice is of utmost importance as it enables technical as well as non-technical personnel to have full control over the website including editing and organization of the website.
Drupal is one such open source CMS that follows a modular, building block approach, allowing unlimited customization. It also allows organizations to build flexible solutions that fit their unique business needs, resulting in a tailored solution specific to their requirement.
Why does it matter?
Indeed, pharmaceutical companies don’t make changes too often in a website. But what if it is company’s information, manufacturing address, representative’s name, regulatory changes or adding new information. Such changes happen as and when required. Therefore, it is pertinent to understand what a good CMS is.
The benefits of a CMS is manifold and leveraging it rightly can be one of the major wins. In a medical device company, there are different stakeholders and they have their own perspective.
Stakeholders involved in the CMS decision
Content Authors - Typically, content developers and consumers are likely to have a different user experience. A medical CMS offers different functionalities to different stakeholders. For authors, it has drag and drops editing, granular content editing, in-place editing, grouping content, sitemap generation, and layout management.
Marketers - For marketers, maintaining a marketing strategy and website goes hand in hand. An effective pharmaceutical website and marketing strategy is always relevant and should be up-to-date. In order to streamline to strategy, marketers make changes too often as per the requirements.
An easy to CMS offers a wealth of undiscovered value far beyond just allowing them to create, distribute and monitor content across the business. The best healthcare CMS is the one that seamlessly integrates with your existing marketing technology stack and overall marketing automation plan.
Business - Evaluating whether your medical device CMS’s feature meets functional and nonfunctional needs is just one thing. Being a decision-makers/business owner you also need to assess the ROI whilst making the decision. Therefore, it's equally important to know how your CMS makes a good business sense. Here are the few questions you should ask yourself before making a decision:
- Does your business require a flexible website
- Do you need to share some common contents on specific or all pages of your website
- Do you need to build connections and stay connected with your customers
- Does your business require your website to be mobile-first
- Do you need to establish and maintain a heavily trafficked site
By identifying these and other issues, you can use your business plan to create a roadmap for a more accurate content strategy.
Developers and IT - When it comes to developing a medical device/healthcare website, it covers a wide area of disciplines. More importantly, you need to look at it from the perspective of development and comparison. Have a look at some of the skills your in-house Drupal developers should have.
Having an in-house team has its own benefit, however, hiring an external support team to have several advantages. A specialized vendor can provide talented individuals, access to technical expertise and scalability, which means the flexibility to scale up and scale down as and when required.
Community - While selecting an open source, it's crucial to look into the community that builds and maintains your medical device CMS of choice. Are they maintaining software quality? Is the CMS viable? Here is our take on why should we contribute back to the community. Also, read why Drupal is a market leader.
What do you get
You can build your brand. Your customers are likely to be loyal, so your employees. You can build a credibility in the market and win the trust of your new customers.
If you want our Drupal team to take a look at your website and provide you with personalized insights. Get in touch.
Leverage Buyer Persona To Enhance Customer Experience
This post is the second in a series of our blog posts covering buyer persona and how to leverage it to enhance customer experience and boost user engagement on your website.
In a B2B or a B2C business, a buyer is not just an abstract idea, but a living being that comes to the marketplace to do business. In order to drive your business in the right order, you need an efficient buyer persona that defines your customer base. You might be wondering what is the role of persona? How it helps in enhancing the digital experience and boost user engagement on the website.
Simply put, a buyer/user persona is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on market research and real data about your existing customers. A detailed buyer persona offers you significant insight for your company and helps you determine where to focus your time, guide product development, and allow for alignment across the organization.
Well, creating user personas is one of the most important steps in building your Drupal website. They help all stakeholders to make better decisions. Let's delve into the process of leveraging buyer persona to make sure we have a fair idea of what is a persona, why do we use it, how does the persona help in marketing strategy and finally, how to create it. We have summarized all of the aforementioned questions so that you should not spend more time googling. Here's everything about user persona.

So how can you leverage buyer persona to enhance the customer experience
Putting your personas to work entirely depends on the concerned authority such as webmaster and web content managers can use it for behavioral tracking to better refine personas based on visitor behavior and activity. It also helps to collect feedback from customer service teams to refresh profiled, and keep them update.
Whereas content marketers can leverage buyer persona to audit and tag their marketing content to analyze where it fits into the buyer journey for various segments.
Using persona insights, marketing leaders can enable programmatic marketing to determine the right content for the right channel at the right stage of the buying process.
A sales rep can use it for sales enablement and understand the various members of the buying committee - what they care about? how to build consensus to close the deal?
Importance of leveraging buyer persona
Personas Cultivate Relationship
Developing a customer-centric design is a must for any business. Here persona acts as a guide, giving you an invaluable information. A detailed persona also helps you cultivate empathy for your clients that lead to a stronger understanding of what they are looking for. Knowing your customers' goal, motivation and behaviors ease your works eventually.
Your Website Is Not For You
Since our focus is clearly on customer needs, developing a design that has them at its core makes more sense. Learning how prospects engage with your brand through its lifecycle gives you perfect metrics to figure out what is working for you and what not.
Before developing a website, try to figure out whether your design reflects the customer’s experience or the company’s operations. Clearly, focused persona designs highlight the road your customers will travel within your business and give you the chance to improve upon them.
Attain Targeted Marketing
Buyer persona helps you to get familiar with your targeted customers. As a result, you will learn stuff, possibly, you don’t know about your customer, gain insights into their perception of your company.
Knowing your prospects helps you in producing market assets using the language they resonate in order to convert them into leads. Perhaps targeted marketing will help you to outperform your competitors.
Gain a Competitive Advantage
Customer-centric web designs are most likely to outperform the generic one. Furthermore, it assists in designing a more captivating website than your competitor, who is using the same generic messaging for everyone.
Evaluate your's as well as your competitor's site through the eyes of a buyer to develop an understanding of competitive positioning. Talk to your digital marketing personnel to do the competitive analysis for your current website.
Futureproof Your Project
For sure, no individual or an organization build website almost every other day but improvise it, enhance it and upgrade it. If you are planning to build a new Drupal website or upgrade it, consider persona research and documentation well before designs are created or your Drupal developer starts working on it.
Identifying customer base will help every stakeholder involved in the project make better decisions. Note that you can never know your customer too well. Once you have a vivid idea of your targets, you can apply that to the product creation, marketing, and business development.
Now go ahead. Design your buyer persona. Let your imagination run.
We, at Valuebound - a Drupal web development company, help enterprises with Drupal migration, Drupal support, third-party integration, performance tuning, managed services and others.
Get in touch with our Drupal experts to have personalized insights on how to enhance user experience and increase engagement on a Drupal website.





