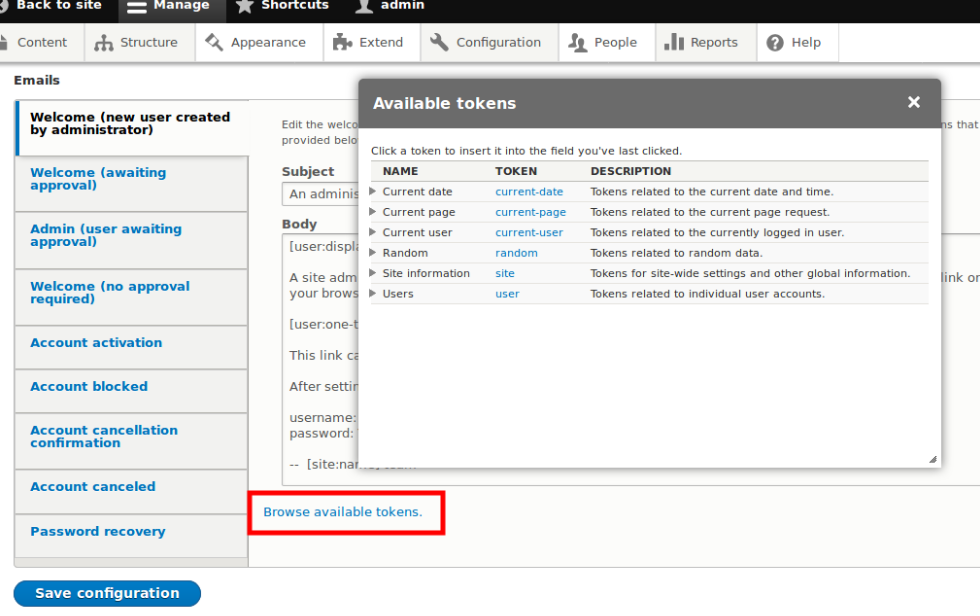
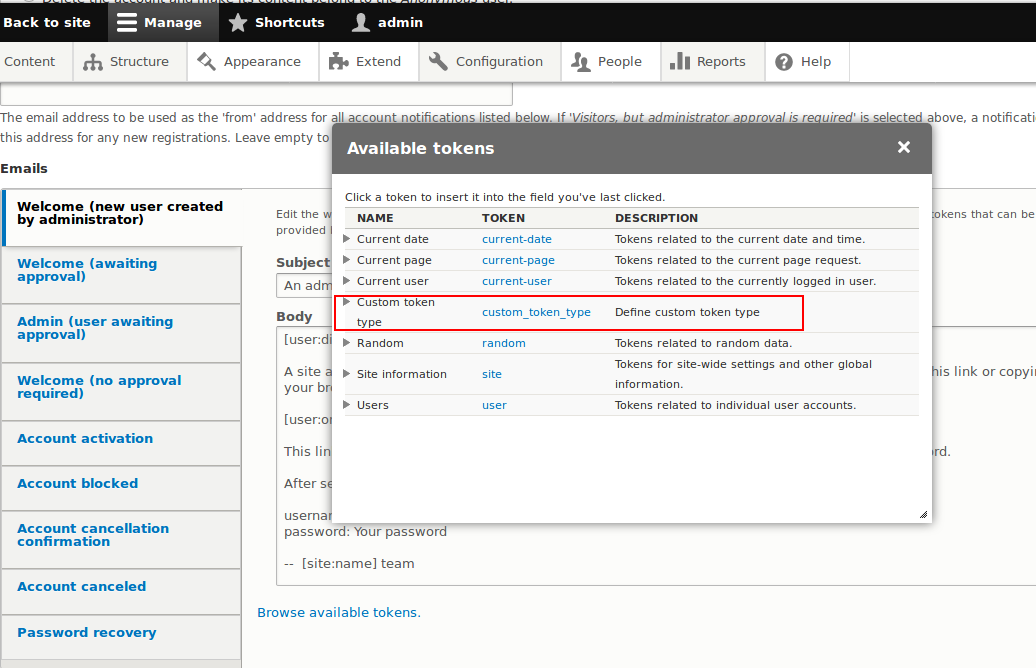
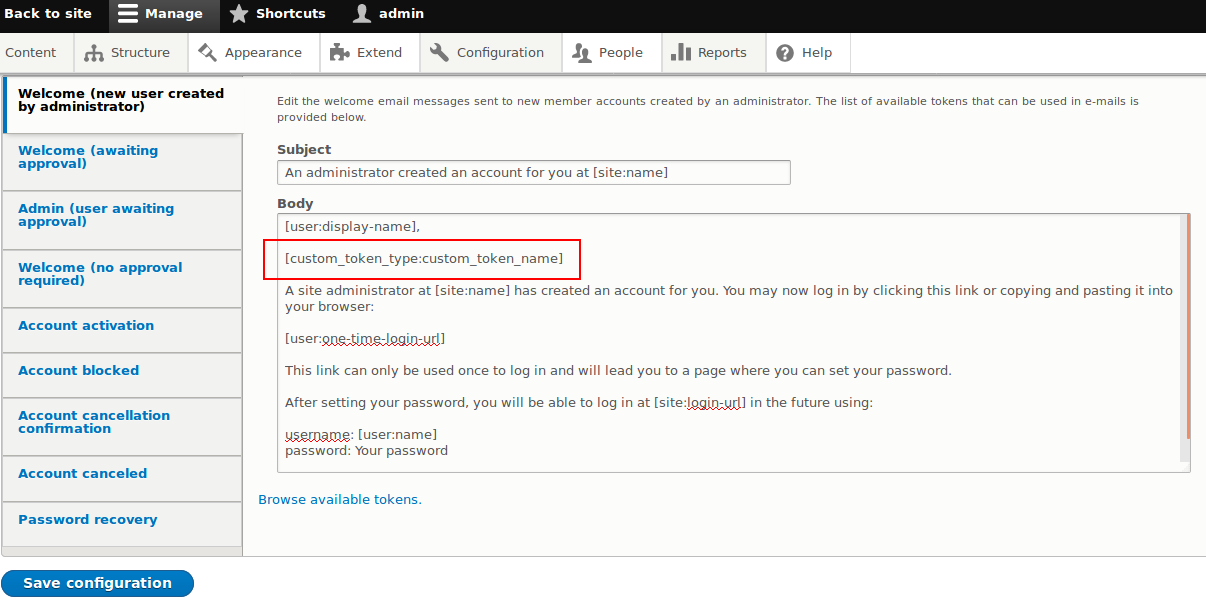
Extend existing field widgets in Drupal 8 application using annotation plugin
Have you ever wondered how the text or email or entity reference field is extended in Drupal 8? Or how to create a custom field/widget/formatter so that it can match with the rest of fields in your Drupal application? This blog will cover everything required to extend existing field widgets in Drupal 8 using annotation plugin.
Many developers, who recently started working on Drupal 8, may not be aware of an entire process so let’s take a closer look to everything step-by-step. Key comparisons between Drupal 7 and Drupal 8, what is an annotation, why annotation and sample use case from an Inline Entity Form step-by-step. After completing this post, you will be able to extend the field with your own methods/functions without disturbing contributed module code.
Note: The below-mentioned functions are used to access properties of available widgets, which are moved to methods on the Widget Plugin Manager.
Comparisons
In Drupal 7
hook_field_widget_info() is replaced by annotation-based plugin
hook_field_widget_settings_form(), hook_field_widget_form(), hook_field_widget_error() : replaced by Widget Interface methods
In Drupal 8
hook_Info is replaced by annotation-based-plugin
public function settings Form(array $form, array &$form_state)
public function formElement(FieldItemListInterface $items, $delta, array $element, array &$form, array &$form_state)
public function errorElement(array $element, ConstraintViolationInterface $violation, array $form, array &$form_state)
Let’s take a brief look at Annotations as it plays a significant role in extending FieldWidgets.
Annotations are one of the new concepts in Drupal 8, which are written as PHP code comments above a class or function. Annotations contain metadata about the function or class.
Note: In Drupal, we have an option to add metadata about the functions inside the comment block so that it can automatically take annotations when Field Widgets rendered on the page. It will help in avoiding multiple files to declare the metadata information.
Why Annotations?
The annotation meta-data lives in the same file and is an integral part of the class that implements the plugin.
This makes it easier to find and to create a new custom plugin by simply copying an existing one.
In addition, Implementation used by Drupal to parse the annotation simply tokenizes the text of the file without including it as a PHP file, so memory use is minimized.
The annotations syntax comes from the Doctrine project, which is nothing but the docblock annotations.
Sample use case from an Inline Entity Form in Drupal 8
Real Entity (node) has been removed from backend when removing contacts field values. Contacts field is an Entity reference field with unlimited cardinality.
By showing this contact with Inline Entity Form - Complex Field Widgets on node edit page.
To avoid this, we need to extend the FieldWidget from an inline entity form - complex. Have a look how to do it programmatically.
Note: Based on the settings, we can control the original entity deletion from the backend. For this, we can use public function settingsForm(array $form, array &$form_state) to add checkbox “Delete referenced node on remove”.
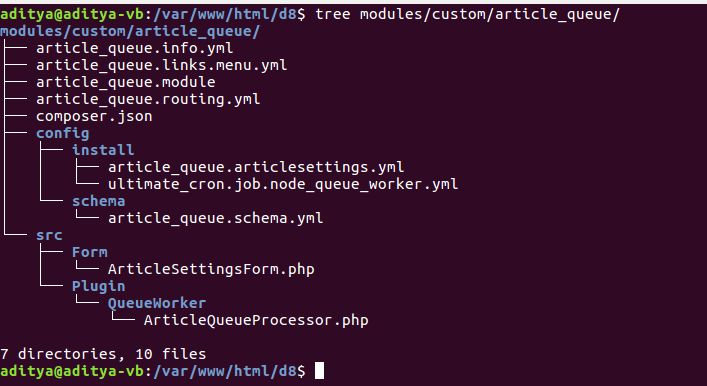
Create a module folder extend_inline_entity_form
Folder Structure: src/Plugin/Field/FieldWidget/ExtendedInlineEntityForm.php
After enabling the module, you can find a similar interface. Here you need to disable “Delete reference node on remove” checkbox to prevent the original node deletion on the backend. Check out the screenshot below for an example.
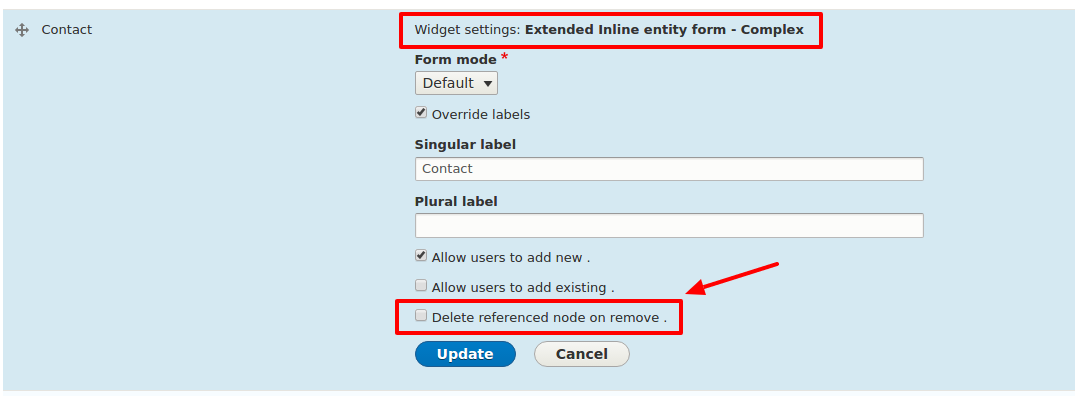
Extending an inline entity form - complex - is nothing, but preventing the deletion of an original node from backend when we remove the entity. With the above-mentioned code, we can unset the widget_state[‘delete’] to stop the deletion of an original node from the backend.
For the above code to work, we need to select the “Delete reference node on remove” checkbox to extend an inline entity form - complex. It can be configurable now! We can add this as a patch to drupal.org or we can contribute this as a sub-module to an inline entity form in Drupal.
That’s it. Hope you can now extend FieldWidgets using an Annotation plugin. If you have any suggestions or queries, please comment down.
Below given is a presentation on extending Field Widgets in Drupal 8.